Guidelines Issued for Critical Mineral Excellence Centres
Why in the News ?
The Ministry of Mines has released guidelines to establish Centres of Excellence under the National Critical Mineral Mission, aiming to boost research and technology in critical minerals essential for clean energy, mobility, electronics, defence, and space sectors.
Strengthening Critical Mineral Research:
- The Ministry of Mines has issued fresh guidelines for setting up Centres of Excellence (CoEs) under the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM).
- The move focuses on enhancing research, innovation, and technology for critical raw materials, which are vital for clean energy, mobility transition, and strategic sectors.
Objectives of the Excellence Centres:
- CoEs will work on developing, demonstrating, and deploying technologies in an end-to-end systems approach to improve Technology Readiness Levels (TRL).
- They will focus on the extraction and beneficiation of critical minerals sourced from diverse origins.
- The initiative promotes targeted research and development (R&D) for securing and strengthening India’s supply chain in the advanced technology and defence sectors.
Role of Academia and Innovation:
- Reputed academic and research institutions will be evaluated and designated as Centres of Excellence.
- These centres will drive innovative and transformative research in the field of critical minerals.
- Emphasis will be placed on interdisciplinary collaboration and cutting-edge solutions to tackle challenges in the critical minerals ecosystem.
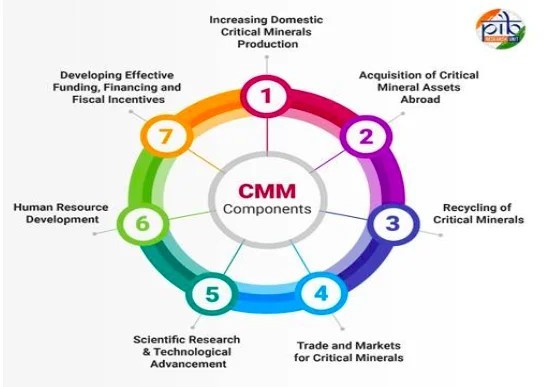
Understanding Critical Minerals :● Definition: Essential for modern technologies and national security; at risk due to limited availability or geographical concentration. ● Criticality: Changes over time depending on demand and supply dynamics. Applications of Critical Minerals: ● Solar Panels: Silicon, tellurium, indium, gallium. ● Wind Turbines: Rare earth elements like neodymium, dysprosium. ● Electric Vehicles (EVs): Lithium, cobalt, nickel. ● Energy Storage Systems: Lithium-ion batteries. ● Also used in electronics, defence, aerospace, and medical tech. Legal and Regulatory Framework: ● 30 Critical Minerals Identified (2022): Includes antimony, lithium, cobalt, etc. ● Part D of Schedule I (MMDR Act, 1957): Grants Central Government exclusive auctioning powers for 24 minerals. ● Centre of Excellence for Critical Minerals (CECM): Reviews mineral list and advises policy. Key Institutions: ● Geological Survey of India (GSI): Leads exploration. ● IREL (India) Limited: Processes beach sand minerals. ● International Cooperation: Collaborations with Argentina, Australia for lithium, cobalt projects. National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM): ● Strategic initiative by the Ministry of Mines for ensuring security and processing of critical minerals. ● Supports clean energy and national security, aligning with India’s net-zero and emissions reduction goals. |