WHO DEFINES PATHOGENS THAT TRANSMIT THROUGH AIR
Why in the news?
WHO introduces the term ‘infectious respiratory particles’ for airborne pathogens, addressing communication challenges during COVID-19 pandemic, enhancing global understanding.
Definition of Airborne Pathogens:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has introduced the term ‘infectious respiratory particles’ (IRPs) to describe pathogens transmitted through the air.
- This terminology aims to address the lack of a standardised term for such pathogens, which posed challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- WHO’s decision follows extensive consultations conducted between 2021 and 2023.
- The lack of uniform terminology previously hindered public communication and efforts to control pathogen transmission.
- The introduction of IRPs as a descriptor seeks to streamline communication and enhance global understanding of airborne transmission.
source:wikimedia
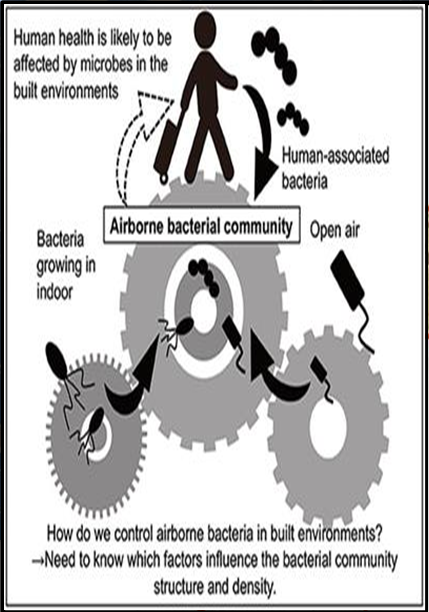
What is Airborne transmission?
|