TEXTILE INDUSTRY CRISIS
Why In the News?
- Textile and garment industry, mainly constituting MSMEs, faces a crisis akin to the late 1960s, according to Indian Cotton Federation (ICF) President J. Thulasidharan.
- Reports indicate shutdowns, machinery disposals, and reduced working hours across the textile value chain.
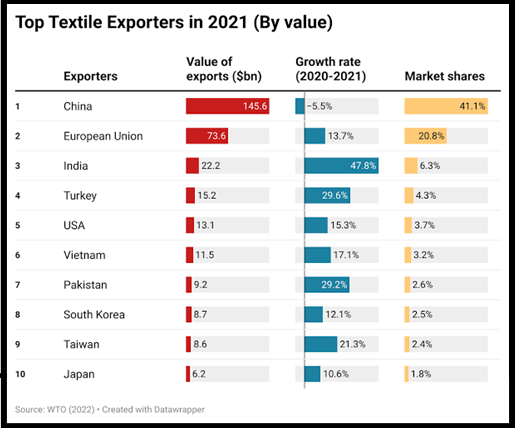
Source: WTO
Factors Impacting Industry:
- Low demand in both domestic and export markets contributes to the prolonged crisis.
- Shipment of textiles declined 0.41% (April-October 2023) YoY, while apparel exports saw an 8.08% decline in October.
- Geo-political situation, inflation, and excessive retailer inventory dampen orders.
Raw Material Challenges:
- Cotton, constituting 60-70% of manufacturing cost, faces fluctuating prices and reduced competitiveness.
- Cotton production and yield in India show a downward trend, impacting the largely cotton-based textile sector.
- Imposition of 10% import duty in 2021 led to fluctuating cotton prices, affecting farmers and the industry.
Quality Control Orders (QCO) Impact:
- Quality Control Orders, especially for Man-Made Fibre (MMF), limit domestic supply, exacerbating industry challenges.
- Escalating input costs, stringent QCO, and import of garments contribute to the multifaceted issues hindering industry growth.
- Stakeholders emphasize the need for consistent and long-term government decisions to benefit both farmers and the consumer industry.
About Textile Production in India:
- India is the 5th largest producer of technical textiles in the whole world with a market size of nearly $22 Bn.
- Cotton, a crucial commercial crop in India, constitutes approximately 25% of global production.
- Cotton is referred to as “White-Gold” due to its economic significance.
The textile industry’s current plight demands comprehensive solutions addressing demand concerns, raw material stability, and policy measures supporting long-term growth.

 Source: WTO
Source: WTO


