SUPREME COURT’S SPLIT VERDICT ON GM MUSTARD
Why in the news?
- Supreme Court’s split verdict on GM mustard approval raises regulatory concerns; judges call for national policy on GM crops.
- Petition challenging environmental release of GM mustard DMH-11.
- Delhi University’s Centre for Genetic Manipulation of Crop Plants (CGMCP) and Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
source:HT
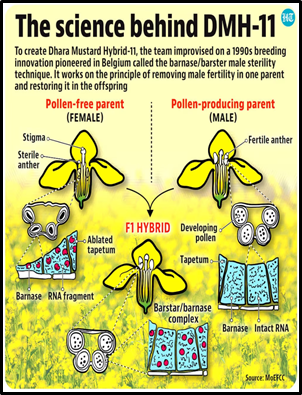
About GM Mustard DMH-11 Development:
- Creation: Crossed Indian variety Varuna with Eastern European ‘Early Heera-2’.
- Yield: 28% higher yield than Varuna.
- Method: Uses Cytoplasmic Male Sterility System; gene transfer from wild mustard.
- Technique: Barnase-Barstar system for hybrid production; makes plant male-sterile and herbicide-resistant.
- Results: 30% higher yield over Varuna; bio-safety field trials conducted between 2010-15.
- Team: Developed by Delhi University’s CGMCP with NDDB and Department of Biotechnology.
What are Genetically Modified (GM) Crops?
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
|