KAKRAPAR UNIT-4 ACHIEVES CRITICALITY
Why in the News?
- The fourth unit of the Kakrapar Atomic Power Project (KAPP) achieved controlled fission chain reaction.
- This marks a significant achievement for the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Ltd. (NPCIL).
Source: Maps Of India
About Kakrapar Nuclear Reactors:
- KAPP’s 700-MWe units are the largest indigenous nuclear power reactors built by NPCIL.
- Pressurised heavy water reactors (PHWRs) utilize natural uranium as fuel and heavy water as a coolant and moderator.
- NPCIL operates existing PHWRs with capacities of 220 MWe and 540 MWe.
- Reactor designs showcase advanced safety features, including steel lining and a passive decay heat removal system.
Indigenous Supply and Execution:
- Indian industries supplied equipment and executed contracts for the two reactors.
- Indigenous capabilities in design, construction, and commissioning of reactors were showcased.
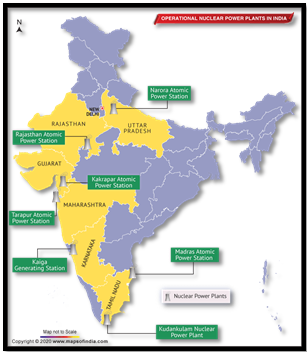
About India’s Nuclear Power Capacity:
Nuclear energy ranks as India’s fifth-largest electricity source, making up approximately 3% of the nation’s total electricity generation.
- Nuclear Reactor Infrastructure:
- India boasts a network of over 22 nuclear reactors spread across 7 power plants nationwide.
- These reactors collectively generate 6780 MW of nuclear power.
- New Addition to the Grid:
- The Kakrapar Atomic Power Project (KAPP-3) reactor was integrated into the grid in January 2021.
- Reactor Types:
- Among the 22 reactors, 18 are Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs), while the remaining 4 are Light Water Reactors (LWRs).
- KAPP-3 Significance:
- KAPP-3 holds a distinctive position as India’s inaugural 700 MWe unit.
- It represents the largest indigenously developed variant of the Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) category.
Current NPCIL Operations:
- NPCIL operates 23 nuclear electricity reactors with a total capacity of 7,480 MWe.
- Nine units, including KAPP-4, are under construction, while 10 reactors in the pre-project phase contribute to a total capacity of 7,000 MWe.

 Source: Maps Of India
Source: Maps Of India


