ISRO’S XPOSAT LAUNCH IN POINTS
Mission Overview:
- ISRO successfully launched XPoSat, India’s first X-ray Polarimeter Satellite, marking the start of the ‘Gaganyaan year.’
- The launch took place from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre using PSLV-C58, placing XPoSat in a precise 650 km circular orbit.
Key Highlights:
- XPoSat is the world’s second X-ray polarimeter mission after NASA’s IXPE launched in 2021.
- It houses two payloads, POLIX and XSPECT, designed by institutions in Bengaluru, focusing on studying X-ray polarization from cosmic sources like black holes and neutron stars.
Source: Nature
| About black holes
· A black hole is a region in space with immense gravitational pull, so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape it. · Formed from the collapse of massive stars, black holes have a singularity at their centre, a point of infinite density. · Their properties defy conventional physics, making them mysterious celestial objects that profoundly influence surrounding space and time. About neutron stars · Neutron stars are remnants of massive stars that have undergone supernova explosions. · Extremely dense, they pack more mass than the Sun into a city-sized radius. Composed mostly of neutrons, they result from the collapse of a star’s core. · Intense gravity on their surface causes exotic phenomena like strong magnetic fields and rapid rotation, making them crucial in astrophysical research. |

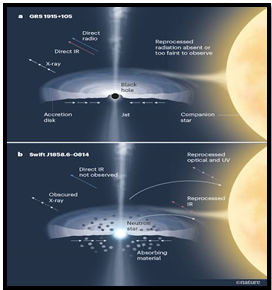 Source: Nature
Source: Nature


