INSPECTION OF POWER PROJECTS UNDER INDUS WATER TREATY
Why in the news?
- The Indian and Pakistani delegations are inspecting power projects in Jammu and Kashmir to ensure compliance with the Indus Water Treaty (IWT).
- This marks the first visit by a Pakistani delegation to Jammu and Kashmir in over five years under the IWT’s dispute settlement mechanism.
Source: Dics
Indus Waters Treaty Overview:
Signing and Background:
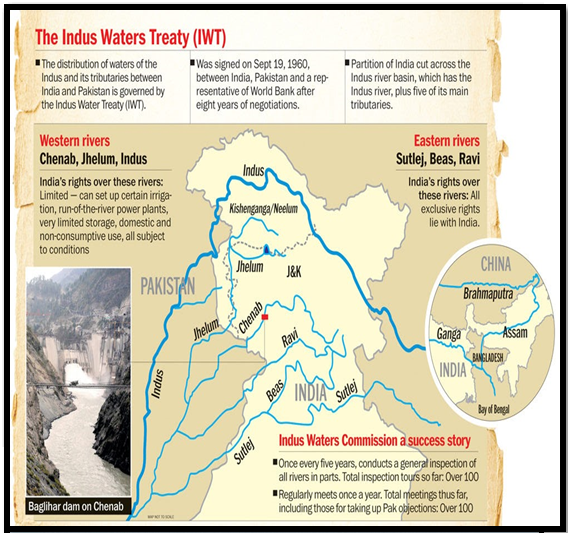
- Signed in September 1960 after nine years of negotiations, involving the World Bank.
- Aims to regulate water use of the Indus River and its tributaries between India and Pakistan.
Key Provisions:
- Water Sharing: Divides the six rivers into eastern and western groups. Pakistan has unrestricted use of the western rivers (Indus, Chenab, Jhelum), while India has similar rights over the eastern rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej).
- Allocation: Pakistan receives 80% of total water, India 20%.
Permanent Indus Commission:
- Establishment: Mandates a Permanent Indus Commission with commissioners from both nations.
- Meeting Requirements: Commissioners meet annually to discuss treaty compliance and water-related issues.
About Indus Water Commission:
|
Associated Article: