India’s Snakebite Crisis: Antivenoms and Lifesaving Solutions
Why in the news?
India’s snakebite crisis claims around 58,000 lives annually. Antivenoms play a crucial role in treating venom, but challenges like rural healthcare access, high costs, and cultural practices hinder effective treatment, requiring urgent improvements in infrastructure and awareness.
The Snakebite Crisis in India:
- India, known as the “snakebite capital of the world,” faces around 58,000 fatalities annually due to snakebites.
- Snake venom contains a deadly mix of haemotoxins, neurotoxins, and cytotoxins that can destroy blood cells, paralyze the nervous system, and damage tissues, making immediate medical intervention
Role and Production of Antivenoms:
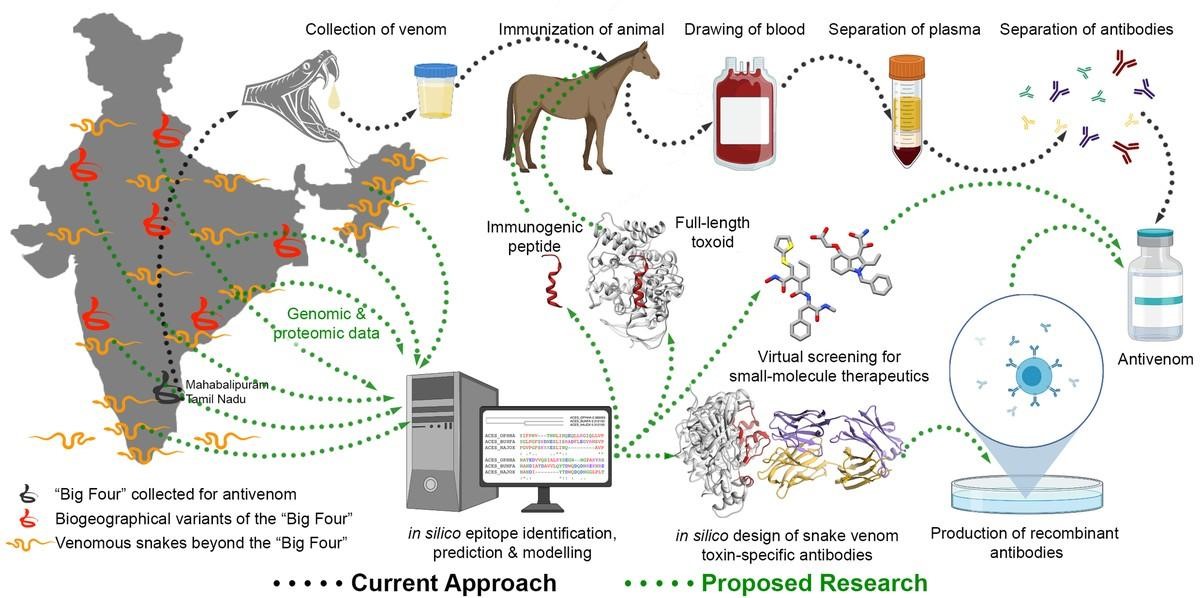
- Antivenoms are critical in neutralizing the venom’s toxins, enabling the body to fight back naturally.
- Production process: Animals like horses are immunized with small doses of snake venom, allowing them to develop antibodies. These are then extracted, purified, and made into antivenoms.
- In India, polyvalent antivenoms are produced to target venom from multiple snake species, although their effectiveness against rare species remains limited.
About Snakebite Envenoming and Antivenoms:
- WHO Classification: Snakebite envenoming is a high-priority neglected tropical disease.
- Global Impact: 1.8 – 2.7 million people envenomed annually.
- Snake Bites in India: 90% of bites caused by common krait, Indian cobra, Russell’s viper, and saw-scaled viper. Around 58,000 deaths from 3-4 million bites annually.
What are Antivenoms?
- Definition: Antivenoms are purified antibodies that neutralize venom.
- Production Process: Horses are injected with venom to produce antibodies; antibodies are collected to treat snakebite victims.
- WHO List: Antivenoms are included in the WHO Essential Medicines List.
Types of Snake Venom:
- Haemotoxic: Affects the cardiovascular system.
- Cytotoxic: Targets specific cells.
- Neurotoxic: Damages the nervous system.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times