India’s First River Dolphin Estimation Reveals 6,327 Dolphins
Why in the News?
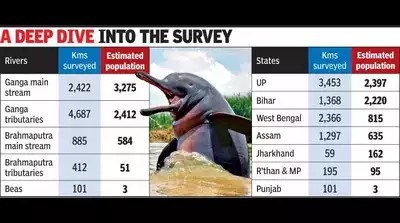
India’s first-ever riverine dolphin estimation recorded 6,327 dolphins across 28 rivers in 8 states. Released at the 7th National Board for Wildlife meeting, the report highlights Uttar Pradesh as having the highest population, emphasizing conservation efforts.
Key Findings of the Report:
- The first-ever riverine dolphin estimation in India recorded 6,327 river dolphins.
- The survey covered 28 rivers across 8 states, with 3,150 man-days spent on fieldwork.
- Over 8,500 kilometers of riverine habitat were surveyed.
- Uttar Pradesh reported the highest dolphin population, followed by Bihar, West Bengal, and Assam.
Survey & Methodology
- The estimation was conducted using scientific methodologies to ensure accuracy.
- It involved collaboration between wildlife experts, forest officials, and conservationists.
- The study focused on species distribution, habitat conditions, and conservation challenges.
Significance & Conservation Efforts
- Released during the 7th National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) meeting at Sasan Gir, Gujarat.
- Prime Minister highlighted the importance of awareness and conservation of river dolphins.
- Findings will help in strengthening policies for dolphin conservation and river ecosystem health.
- Supports India’s commitment to biodiversity preservation and aquatic ecosystem protection.
Dolphin Characteristics:
- Ganges river dolphins are adapted to freshwater ecosystems.
- They are functionally blind and use echolocation for navigation and hunting.
- These dolphins surface every 30 to 120 seconds to breathe.
- They usually live alone or in small groups.
- Mothers give birth to one calf every 2-3 years.
Ecological Significance
- Ganges river dolphins are India’s National Aquatic Animal.
- They serve as key indicators of river health.
- Their presence reflects the overall condition of the river ecosystem.
- Conservation is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and sustaining the Ganga River.
Major Threats & Conservation
- Threats: Accidental fishing gear entanglement, poaching for oil, habitat destruction, and pollution.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Project Dolphin and Vikramshila Ganges Dolphin Sanctuary protect their habitats.
- National Ganga River Dolphin Day (5th October) promotes awareness.