INDIAN NBFCS TO RAISE FUNDS ABROAD AMID TIGHT LIQUIDITY
Syllabus:
- GS 3:
- Indian Economy and related issues.
- Banking and financial sector polices and reforms.
Why in the News:
Non-banking economic corporations (NBFCs) in India are increasingly turning to offshore borrowing due to tight domestic liquidity and rising borrowing charges. Regulatory modifications by means of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and heightened competition in the domestic bond market have made distant places fundraising a greater feasible and essential choice for these institutions.
Source: ET
Rising Costs in Domestic Borrowing:
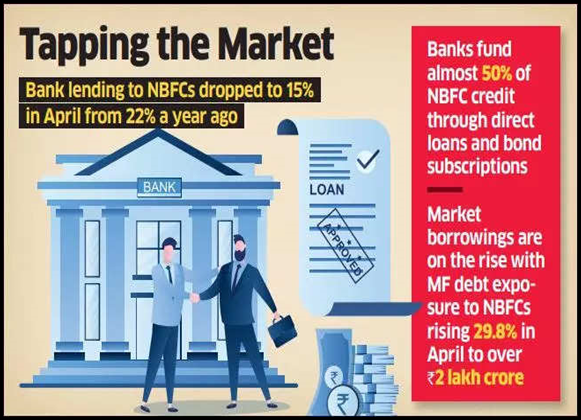
- Increased Costs: Liquidity situations in India have tightened, making domestic borrowing an expensive affair for non-banking economic corporations (NBFCs). Elevated interest rates and a surge in domestic bond issuances have pushed up borrowing fees
- Regulatory Impact: The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) decision in November 2023 to raise risk weights for financial institution(Banks) lending to NBFCs has led to a significant growth in borrowing prices for these entities.
- Market Competition: Higher borrowing of banks and NBFCs throughout the Domestic market has intensified competition, and is riding up costs for NBFCs seeking to raise funds locally.
- Fund Diversification: To cope with the steeply-priced domestic borrowing surroundings, NBFCs are increasingly more turning to remote (overseas) markets to diversify their funding profiles, as encouraged by regulatory guidelines.
- Capital Raising Strategies: In response to those demanding situations, NBFCs like Shriram Finance, Bajaj Finance, and others are exploring alternate funding avenues, along with offshore bonds and External Commercial Borrowing (ECBs).
Overseas Borrowing as a Solution:
- Offshore Bonds : VArious NBFCs since the begining of 2024 have resorted to raise funds through various tranches of offshore bonds to benefit from lower intrest rates abroad.
- Global Banking Offers: Global banks are providing competitive pricing for hedging fees, making remote places borrowing even greater appealing for NBFCs compared to home alternatives.
- US Fed Impact: Despite the US Federal Reserve not lowering fees as anticipated, NBFCs preserve to find overseas borrowing extra favorable due to the relatively decrease expenses involved.
- Funding Pipeline: Industry professionals recommend NBFCs to hold a constant funding pipeline, with a focal point on preserving their stability sheets strong and keeping get admission to to capital.
- Diversification Mandate: The RBI has repeatedly warned NBFCs approximately the concentration of their investment profiles, pushing them to explore and undertake various funding sources to mitigate dangers.
About Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC)
- Definition: NBFCs are companies registered under the Companies Act, 1956, involved in lending, investment in securities, leasing, lease-buy, insurance, and chit finances.
- Exclusions: They do not engage in agriculture, industrial activities, trading of products, or real estate transactions.
- Deposits: NBFCs broadly speaking accept time deposits and not demand deposits, with phrases among 12 and 60 months, and interest rates capped at 12.5% with the aid of RBI.
- Restrictions: NBFCs lack banking licenses, can’t issue cheques, participate in payment systems, or provide deposit coverage like banks.
- Regulation: Managed by means of the RBI and the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
Strategic steps by NBFCs
- Crisis Management: NBFCs like Shriram Finance have been actively managing their liability stacks to avoid liquidity crunches, with plans to raise massive funds via FY25 to satisfy debt responsibilities.
- Alternative Avenues: Many NBFCs have started to seek approvals for offshore investment as a part of their strategy to keep away from the crowded domestic marketplace and leverage higher phrases internationally.
- Investor Sentiment: The trend of elevating funds abroad has also been pushed investor self assurance in these companies’ capacity to manage and sustain increase through varied investment assets.
- Long-Term Plans: NBFCs are searching at a 2-3 yr horizon to gradually growth the percentage of foreign places borrowing in their total liabilities, ensuring financial balance.
- Mobile Deployment: With the RBI’s cognizance on stopping over-reliance on domestic investment, NBFCs are also deploying capital raised abroad to aid business enlargement and reduce vulnerability to neighborhood market fluctuations.
Impact of RBI’s Warnings
- Liability Management: NBFCs are actually more careful approximately dealing with their liabilities to make sure they could meet quick-time period obligations without straining their stability sheets.
- Crowded Market: The domestic bond marketplace has visible a surge in issuances, making it extra tough for NBFCs to secure favorable phrases compared to worldwide markets.
- Competitive Edge: NBFCs raising funds in foreign market are gaining a competitive area by locking in lower charges, which helps them provide more attractive deposit fees and economic merchandise regionally.
- Strategic Shifts: In mild of the RBI’s warnings, NBFCs are more and more trying to diversify their funding resources to reduce reliance on any unmarried marketplace, thereby improving their monetary resilience.
- Growth Strategies: With a various investment base, NBFCs are higher placed to pursue boom techniques, consisting of increasing into new markets and offering progressive economic products.
Future Outlook
- Continuous Monitoring: The RBI is expected to keep tracking NBFCs’ funding strategies intently, with a focus on ensuring that these agencies do no longer become over-reliant on any unmarried source of funding.
- Regulatory Compliance: NBFCs will want to align their funding techniques with regulatory expectations, making sure that they preserve a balanced and sustainable investment profile.
- Expansion Plans: As NBFCs steady greater price range from overseas places markets, they are possibly to accelerate their growth plans, domestically and across the world, to capitalize on growth possibilities.
- Market Dynamics: The shift toward overseas borrowing should regulate the dynamics of the domestic bond market, potentially leading to adjustments in how different economic establishments approach their funding techniques.
- Long-Term Stability: By diversifying their funding sources and carefully coping with their liabilities, NBFCs are positioning themselves for long-time period economic stability and sustainable increase.
- Steady Pipeline: NBFCs like Piramal Capital are committed to preserving a consistent pipeline of offshore finances to make sure access to capital during both favorable and difficult market conditions.
- Insurance Policy: Raising finances overseas, together with Piramal Capital’s $300 million maiden offshore bond, is visible as an “insurance policy” to keep away from liquidity shortfalls, with plans to grow overseas borrowing to 10-15% of total liabilities.
Conclusion
The shift to offshore borrowing by means of NBFCs underscores the continuing challenges in India’s domestic financial markets, driven via tighter liquidity and regulatory pressures. This method displays a broader want for diversification and monetary resilience, ensuring that NBFCs maintain get admission to to capital whilst navigating complex market conditions.
Source: The Mint
Mains Practice Question
Question: Discuss the reason behind the growing trends of Indian NBFCs raising funds abroad. What are the potential advantages and risks related to this shift in their investment approach? How should regulators address this challenge?