INDIA TO RAMP UP TRADE NEGOTIATIONS WITH KEY PARTNERS
Relevance: GS 2 – Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Why in the news?
- India and Australia will review their Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement from 19-22 August.
- The ninth round of FTA talks with the EU is scheduled for 23-27 September.
- The next round of FTA talks with the UK is yet to be finalised.
- Reducing trade barriers through FTAs can boost India’s global competitiveness. FTAs drive domestic reforms, diversifying export markets. They create jobs and strengthen strategic alliances.
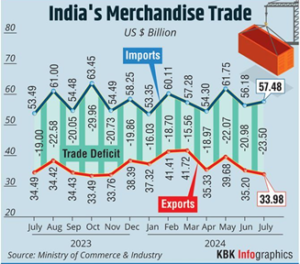
India’s Trade Deficit
- Overall Trade Deficit: India’s trade continues to be in deficit, driven by slowing export growth amid decreased global demand and falling commodity prices.
- Merchandise Trade Deficit: July 2024: The merchandise trade deficit widened to $23.5 billion as exports declined and imports increased sequentially.
- Merchandise Exports: In FY24, India’s merchandise exports stood at $437.06 billion, down from $451.07 billion in the previous fiscal year (FY23).
- Goods Imports: Goods imports decreased to $677.24 billion in FY24 from $715.97 billion in FY23.
India’s Intensive Trade Negotiation
The union commerce ministry has outlined a rigorous trade negotiation schedule starting next week, aiming to finalise agreements with key partners such as the EU, Australia, and ASEAN.
- Australia-India CECA: Scheduled from 19-22 August, India and Australia will review their Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA).
- India – EU FTA: The ninth round of FTA negotiations with the EU is set for 23-27 September.
- India- Peru FTA: India will engage in the next round of FTA talks with Peru in September.
- India – ASEAN Trade Agreement: Scheduled from 19-22 November, India will review its trade agreement with ASEAN. India will review tariff concessions granted to ASEAN members, including Vietnam, which benefits from zero-tariff imports of mobile phone components.
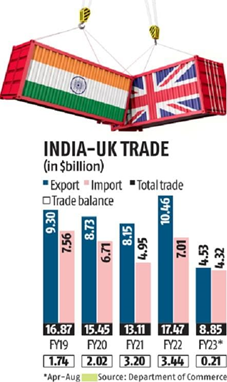
- India – UK FTA: The next round of FTA talks with the UK has not been finalised, with India seeking an exemption from the UK’s carbon tax.
- India – Oman FTA: An FTA with Oman is likely to be announced soon as negotiations are nearing completion.
Key Issues on India-EU Trade Agenda
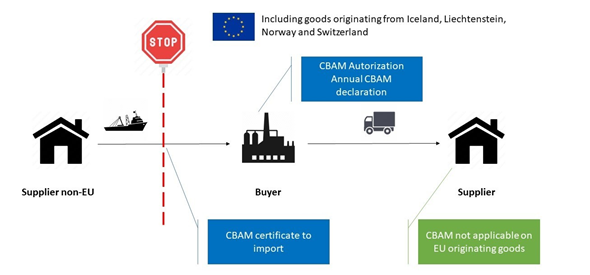
- Carbon Tax (CBAM): India is focused on the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), commonly known as the carbon tax.
- Pesticide Residue Levels: India is advocating for relaxed rules on the maximum pesticide residue allowed in agricultural commodities.
- Tariff Line Eliminations: India seeks to eliminate tariff lines on most products, including processed food and readymade garments.
- EU’s Demands:
- Tariff Cuts: The EU is pushing for tariff reductions on its key exports, such as automobiles, wines, and spirits.
- Market Access: The EU wants greater access to India’s banking, insurance, and e-commerce sectors.
- Intellectual Property Protection: The EU advocates for stronger intellectual property protections, which India views cautiously, particularly regarding generic medicines.
- Sustainability and Labour Standards: The EU is pressing for higher sustainability and labour standards, raising concerns in India about potential impacts on domestic regulations and industries.
- Services Sector:
- EU’s Access: The EU seeks greater access to India’s banking, insurance, and e-commerce sectors.
- India’s Push: India is striving for unrestricted access to its IT and professional services in the EU market.
India-UK FTA Key Issues
UK’s Demands: The UK is advocating for zero tariffs on Scotch whisky, electric vehicles, and chocolates. Also, The UK wants India to liberalise its telecom, finance, and legal sectors.
India’s Position:
- India is unlikely to offer zero duty on Scotch whisky but is considering offering a tariff structure similar to the one provided to Australia.
- For example, tariffs on wine from Australia were reduced from 150% to 100% on implementation, and further down to 50% over 10 years for bottles priced at a minimum of $5. For bottles priced at a minimum of $15, tariffs were reduced to 75% initially and then to 25% over a decade.
- India seeks duty-free access for its textiles and pharmaceuticals in the UK market.
- India is advocating for more work visas and mobility rights for its professionals. The UK has tentatively agreed to fixed-period visas but is hesitant on the number of visas to be issued.
- India has requested an exemption from the UK’s 2027 carbon border tax, a contentious issue that remains unresolved.
- Other Negotiation Points:
- Rules of Origin: The two countries are working on finalising rules of origin.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Discussions on intellectual property rights are ongoing as part of the FTA negotiations.
India-Australia CECA Key Issues
- Non-Tariff Barriers: India is pushing to remove non-tariff barriers that restrict the export of agricultural products like okra, pomegranate, and grapes to Australia, despite Australia agreeing to zero tariffs on these products.
- Negotiation Rounds: Nine formal rounds and inter-sessional meetings have been held, with negotiations based on five tracks agreed under the Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA) and 14 new areas including micro, small and medium businesses, innovation, agri-tech, and critical minerals.
- Tariff Lines: India has allowed access to Australian products covered under 70% of tariff lines. Whereas Australia has agreed to eliminate tariffs on all products from India but is seeking further tariff cuts from India on additional products.
- Pharmaceuticals Pricing Concerns: Discussions are ongoing about pharmaceutical pricing controls on generic medicines in Australia, which is a major concern for India.
- Rules of Origin – Ongoing Negotiations: The rules of origin were not fully negotiated when the CECA was signed, and both sides are now working on finalising product-specific rules.
- Mutual Recognition Agreements (MRAs): Challenges remain in areas related to investment and services, including the establishment of MRAs and market access for service sectors.
Importance of FTAs for India
- Global Competitiveness: FTAs are crucial for enhancing India’s global competitiveness, especially in a challenging global environment.
- Economic Growth: These agreements open new markets, boost exports, and attract foreign investment, driving economic growth.
- Strategic Alliances: FTAs help India diversify export markets, create jobs, and strengthen strategic alliances, making them a key tool in its economic and geopolitical strategy.
- Negotiation Challenges: FTAs are complex and involve protracted negotiations, but India and its partners, like the EU, are committed to overcoming these challenges to realise the potential benefits.
Way Forward for India’s Trade Negotiations
- Enhance Market Access: Advocate for greater access to Indian markets for foreign goods and services while ensuring reciprocal access for Indian exports.
- Promote Domestic Reforms: Implement necessary domestic reforms to align with international standards and enhance competitiveness in global markets.
- Diversify Export Markets: Actively seek to open new markets through FTAs to reduce dependency on traditional trading partners.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve industry stakeholders and trade experts in the negotiation process to ensure comprehensive representation of interests.
- Monitor Trade Deficit: Continuously assess the trade deficit and adjust negotiation strategies to enhance export performance and reduce import reliance.
- Address Non-Tariff Barriers: Work towards the removal of non-tariff barriers that hinder trade, particularly in agricultural exports.
- Strengthen Strategic Alliances: Use FTAs as a tool to build strategic alliances that can enhance geopolitical stability and economic collaboration.
Alternative articles
https://universalinstitutions.com/investment-lessons-from-the-india-efta-trade-deal/
Mains question
Discuss the implications of India’s widening trade deficit in the context of India signing a free trade agreement with various nations. How does this impact India’s economic stability and growth prospects? (250 words)