Hypertension
Context: The Indian National Health Portal reports that 30% of adult Indians have elevated blood pressure — a little higher in urban (34%) compared with rural (28%) areas.
More on the news
- Effectively, high blood pressure is occurring in one in three or four children, and this is much higher than earlier estimates of about 7%.
- Hypertension is often clustered with other cardio-metabolic risk factors including overweight and obesity.
- Adolescents with high fasting blood glucose, hemoglobin A1c, serum triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels also have a greater risk of high blood pressure.
What is hypertension?
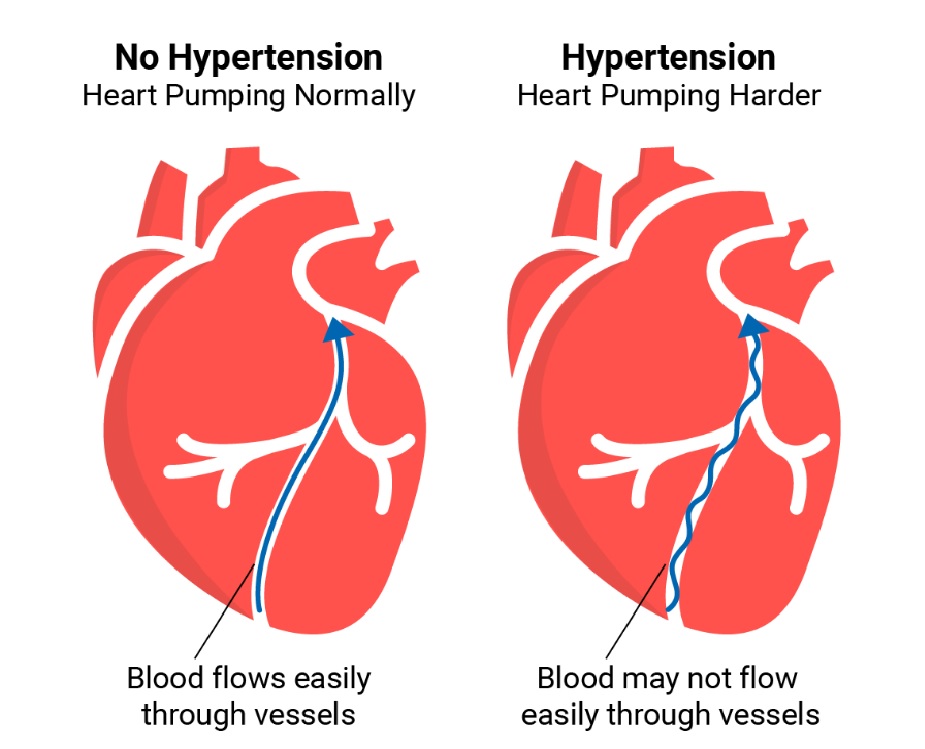
- Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of the body’s arteries, the major blood vessels in the body. Hypertension is when blood pressure is too high.
- Blood pressure is written as two numbers. The first (systolic) number represents the pressure in blood vessels when the heart contracts or beats
- The second (diastolic) number represents the pressure in the vessels when the heart rests between beats.
What are the Risks associated with High Blood Pressure?
- High blood pressure can damage your arteries by making them less elastic, which decreases the flow of blood and oxygen to your heart and leads to heart disease. In addition, decreased blood flow to the heart can cause Chest pain, also called angina.
- Heart attack, which happens when the blood supply to your heart is blocked and heart muscle begins to die without enough oxygen. The longer the blood flow is blocked, the greater the damage to the heart.
- Heart failure, a condition that means your heart can’t pump enough blood and oxygen to your other organs.
- High blood pressure can cause the arteries that supply blood and oxygen to the brain to burst or be blocked, causing a stroke. Brain cells die during a stroke because they do not get enough oxygen. Stroke can cause serious disabilities in speech, movement, and other basic activities.
- Having high blood pressure, especially in midlife, is linked to having poorer cognitive function and dementia later in life.
- Adults with diabetes, high blood pressure, or both have a higher risk of developing chronic kidney disease than those without these conditions.
What are the causes for hypertension?
Modifiable Risk include
- Unhealthy diets (excessive salt consumption, a diet high in saturated fat and trans fats, low intake of fruits and vegetables), Physical inactivity,
- Consumption of tobacco and alcohol, and Being overweight or obese.
Non-modifiable risk factors include
- A family history of hypertension,
- Age over 65 years and co-existing diseases such as diabetes or kidney disease.
What can I do to prevent or manage high blood pressure?
- Many people with high blood pressure can lower their blood pressure into a healthy range or keep their numbers in a healthy range by making lifestyle changes.
- Getting at least 150 minutes of physical activity
- Not smoking
- Eating a healthy diet, including limiting sodium (salt) and alcohol
- Keeping a healthy weight
- Managing stress
| Practice Question
1. What are the risks associated with Hypertension? What can be done to overcome it? |