Gum Arabic: A Vital Natural Resource with Global Demand
Why in the News?
Amid global supply chain disruptions, Sudan’s dominant gum Arabic exports face challenges, impacting industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics that rely on this key emulsifier, stabilizer, and binding agent.
About Origin and Global Production:
- Gum Arabic is a dried, water-soluble exudate mainly obtained from two acacia species—Acacia senegal and Acacia seyal.
- These trees are native to North Africa and flourish in the sub-Saharan Sahel region, as well as in parts of Australia, India, and South America.
- In India, senegal is found in southeast Punjab, the northern Aravalli hills, Rajasthan, and Gujarat.
- Sudan leads global production with a 70% market share, followed by Cameroon, Chad, Mali, and Nigeria.
- Historically, gum Arabic was used in ancient Egyptian embalming practices, while today, it serves multiple industries.
Composition and Properties
- Gum Arabic is a neutral or mildly acidic polysaccharide salt containing calcium, magnesium, and potassium cations.
- It is non-toxic, odorless, and tasteless, making it suitable for food applications without affecting sensory qualities.
- It dissolves easily in water, forming a clear, mucilaginous solution, but is insoluble in oils and most organic solvents.
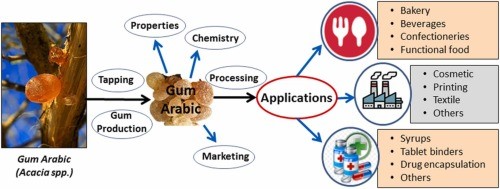
Industrial and Commercial Uses
- Gum Arabic plays a crucial role in the food industry, acting as a stabilizer, emulsifier, and thickener in products like confectionery, beverages, and dairy items.
- It is widely used in ceramics, painting, photography, and printmaking due to its binding properties.
- With its exceptional solubility and versatility, gum Arabic remains a valuable natural resource in multiple global industries.
Key points: Gum Arabic
- A natural resin derived from Acacia trees found in the Sahel region of Africa.
- Functions as a stabilizer, emulsifier, and thickening agent in various industries.
Usage of Gum Arabic
- Food & Beverages: Prevents ingredient separation in soft drinks, candies, and baked goods.
- Cosmetics: Enhances lotions, creams, and makeup consistency.
- Pharmaceuticals: Acts as a binding agent in medicines and capsules.
- Printing & Textiles: Improves ink and dye adhesion.
Global Presence & Significance
- Sudan supplies 70% of global demand, with Chad, Nigeria, Senegal, and Mali as smaller producers.
- No viable substitute, essential for carbonated drinks.
- A major export commodity for Sudan, impacting global supply chains.
- Disruptions in Sudan affect multinational corporations like PepsiCo and Coca-Cola.