Giving the urban Indian a better life
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 Role of women and women’s organization, population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues, urbanization, their problems, and their remedies.
- Tags: #Urbanization #Urbanlife #Pollution #GS2 #UPSC
Why in the news?
- Theme of World Cities Day 2023 (31st October): “Financing Sustainable Urban Future for All”.
- The primary objective is to address the need for channeling finances effectively to support sustainable urban development.
- Focus on preventing the detrimental consequences of flawed urbanization.
- Strive to create cities that are both livable and safe for all residents.
- Alarming Pollution Statistics
- Findings by The Energy Policy Institute at Chicago (EPIC) reveal that 39 out of the top 50 most polluted cities globally are situated in India.
- Pollution in India directly impacts public health and life expectancy.
- On average, an Indian loses 5.3 years of life expectancy due to pollution, with residents of Delhi suffering a staggering loss of 11.9 years.
Health Consequences
- Pollution-related health issues include burning eyes, nasal and throat irritation, persistent coughing, breathing difficulties, and increased asthma cases.
- Moreover, it contributes to the onset of cardiovascular diseases, posing significant risks to the population’s overall health.
- Air Quality Crisis in Mumbai: Recent media reports have labeled the air quality in Mumbai as “Death by Breath” due to extremely unsatisfactory Air Quality Index (AQI) levels.
- This term underscores the severity of the air quality problem in the city and its detrimental impact on public health.
- Expanding Pollution Beyond Indo-Gangetic Plains: Traditionally, poor air quality in India was primarily associated with the Indo-Gangetic plains, attributed to factors such as temperature inversion and reduced wind speeds.
- However, the issue of air pollution is now extending to India’s coastal cities, indicating a broadening crisis.
- Key Factors Contributing to Pollution: Pollution in Indian cities is exacerbated by factors such as road dust, concrete batching, and polluting industrial units.
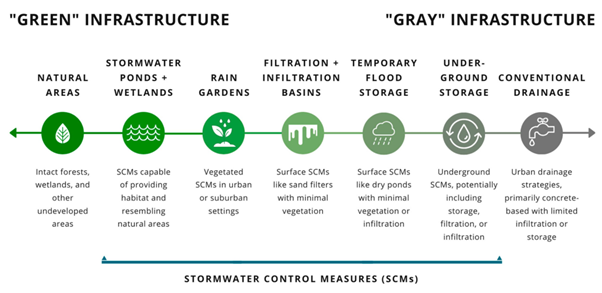
Expansion of ‘Gray’ Infrastructure
- Definition of Gray Infrastructure: It encompasses human-engineered structures and systems related to water resources management. It includes facilities like water treatment plants, wastewater treatment plants, pipelines, and dams.
- Gray infrastructure is a vital part of centralized approaches to water management.
- Components of gray infrastructure involve man-made structures designed for water treatment, distribution, and control.
- These components are crucial for ensuring the availability, quality, and regulation of water resources.
- Grey infrastructure plays a significant role in supporting urban and industrial water supply, as well as wastewater treatment processes.
- Rapid growth of ‘gray’ infrastructure is a critical issue in Indian cities.
- This expansion includes a focus on real estate development, wider roads, and increased vehicular traffic.
- They have encroached upon spaces meant for pedestrians and reduced green cover in urban areas.
- The proliferation of motorized transport, responsible for 60% of urban pollution, is a significant contributor.
- Neglect of green spaces like water bodies, urban forests, and urban agriculture has led to a loss of ecological balance.
- Components of gray infrastructure involve man-made structures designed for water treatment, distribution, and control.
Seasonal Smog and Automobile Growth
- During North India’s winter, the burning of paddy straw (Parali) adds to the problem of smog and particulate matter.
- The growth of the Indian automobile market, projected to reach $160 billion by 2027, further exacerbates urban pollution.
- The increase in vehicle sales calls for a reevaluation of urban development strategies.
Inadequate Construction Regulation
- Construction activities, on the rise in Indian cities, contribute to around 10% of air pollution in regions like the National Capital Region.
- The absence of effective monitoring and control measures for construction activities is a concern.
- City residents lack meaningful participation in the urbanization process and often have limited influence on decision-making.
Urban Development
- Effective Resource Allocation: Emphasize the importance of directing financial resources to the right areas.
- Sustainable Urban Development: Highlight the need to invest in projects that promote sustainability and environmental consciousness.
- Infrastructure and Services: Ensure that funds support the development of essential urban infrastructure and services.
- Health Implications: Discuss the serious health consequences of air pollution on urban populations.
- Life Expectancy Reduction: Address the alarming fact that air pollution significantly reduces life expectancy.
- Safety Measures: Stress the importance of implementing measures to make cities safer for their inhabitants.
Promoting Public Transport
- Emphasize the need for a new city-building strategy that prioritizes public transportation, secure pedestrian pathways, and bicycle lanes.
- Suggest the creation of bicycle officers to oversee and promote cycling as an eco-friendly mode of transport.
- Advocate for regulating construction activities through standardized operating procedures.
- Investment in Public Transport: Highlight the necessity for substantial investment in public transport systems, including buses, to meet the growing demands of urban mobility.
- Estimate a requirement of approximately 10 lakh additional buses for urban areas.
- Stress the importance of making public transport accessible and affordable, especially for the 85% of people employed in the informal sector.
- Controlling Private Vehicle Usage: Propose the implementation of measures to control private motorized vehicle movement within cities.
- Suggest the possibility of imposing a congestion tax on private car owners during peak hours.
- Mention the odd-even number plate formula as another intervention option to reduce traffic congestion.
Air Quality Response Plans
- Refer to Delhi’s Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) as an example of a mechanism to address air pollution promptly based on air quality levels.
- Encourage other Indian cities to adopt similar air quality response plans tailored to their specific needs.
Real-time Monitoring and Community Involvement
- Advocate for a zero-tolerance policy towards industrial pollution and the implementation of real-time monitoring.
- Stress the importance of involving local residents in street supervision and proactively addressing pollution issues.
Preserving Urban Commons
- Highlight the significance of protecting urban commons, including ponds, water bodies, urban forests, parks, and playgrounds.
- Urge urban communities to take an active role in nurturing and expanding these green spaces.
Ecological Wisdom in Urban Development
- Contrast current urban development practices with Ian McHarg’s vision in his book “Designing with Nature,” which advocated ecological wisdom in landscape planning and design.
- Express concern over the ongoing massive land use changes and the conversion of open spaces for real estate development, resulting in pollution.
- Emphasize the importance of meaningful afforestation within cities to combat pollution, rather than planting trees far away from urban areas.
Empowering Governance
- Address the limitations of cosmetic solutions like smog towers and road watering by focusing on governance strengthening.
- Advocate for people’s empowerment through effective city governance structures.
- Promote the widespread availability and adoption of pollution guides and standard operating procedures (SOPs) for various government departments and agencies.
Public Participation
- Encourage public engagement in governance by supporting the implementation of measures like the odd-even number plate formula and a ‘no-car day’ each week.
- Cite the successful enforcement of SOPs during the COVID-19 pandemic as an example of what can be achieved through collective action.
- Stress the importance of a comprehensive and effective Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)-like SOP for pollution control.
Medical Community’s Role
- Emphasize the role of the medical community in supporting public health advisories related to air pollution.
- Highlight the urgency of addressing air pollution as it directly impacts public health and life expectancy.
- Recognize that the poor and marginalized segments of the population, despite being minimal contributors to pollution, are the most vulnerable and require concerted efforts for a better quality of life.
Source: The Hindu
Mains Question
Discuss the significance of grey infrastructure in modern water resource management and the challenges associated with its implementation.