FROM WARP SPEED TO RESET: THE STATE OF INDIA-U.S. TIES
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- India and its Neighbourhood- Relations.
- Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s upcoming engagement with U.S. President Joe Biden at the G-7 summit, along with the recent complexities in India-U.S. relations, has brought renewed focus on the need for strategic resets and diplomatic efforts to maintain and enhance bilateral ties.
Source: Sourcenet
Overview of the Past Year
- Prime Minister Modi’s U.S. Visit: A year ago, Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s state visit to the U.S. was marked by significant strategic and technological cooperation announcements.
- Jet Engine Technology Transfer: The U.S. offered to restart the decade-old plan to transfer jet engine technology to India, highlighting high-tech cooperation.
- Critical and Emerging Technology (CET): The U.S.-India initiative on CET was seen as a major success, aiming to enhance bilateral relations.
- Expectations vs. Reality: Despite the high ambitions set during the visit, the relationship’s pace over the past year has not matched these expectations due to various internal and external factors.
- Upcoming Engagements: The newly sworn-in Indian Prime Minister will engage with the U.S. President at the G-7 outreach summit in Italy, with senior U.S. officials also visiting Delhi soon.
The Crests: Highlights of India-U.S. Relations
- 25 Years of Turnaround: Last September marked 25 years since the turnaround in India-U.S. ties post-Pokhran, highlighted by PM Atal Bihari Vajpayee’s speech calling India and the U.S. “natural allies.”
- Strategic Ties: Over the years, strategic ties have strengthened with dialogues in various spheres, including climate change, green energy, and outer space.
- Military Cooperation: The past decade has seen significant growth in strategic trust, with foundational agreements, numerous military exercises, and considerable military hardware purchases.
- De-Hyphenation from Pakistan: Old irritants, such as U.S.-India ties being linked with Pakistan, have diminished, allowing for more focused bilateral relations.
- Indo-Pacific Strategy and Quad: Shared concerns over China’s aggression and India’s increased engagement with the Quad and the U.S.’s Indo-Pacific strategy have aligned Delhi and Washington’s international stances.
The Troughs: Challenges in the Relationship
- Multilateral Cooperation Issues: Differences in approach to global conflicts, such as Russia’s war in Ukraine, highlight areas of disagreement, with the U.S. framing the war in terms of international law and humanitarian principles, while India considers historical and Global South impacts.
- Russia Relations: The U.S. has moderated its objections to India’s purchase of Russian oil, while India has postponed its annual India-Russia summit, reflecting a complex balancing act.
- Moralistic Posture: The U.S.’s support of Israel’s actions in Gaza, despite international calls to stop, has affected its moral stance, complicating relations.
- Lack of High-Level Engagement: Planned high-level visits, such as those by U.S. National Security Adviser Jake Sullivan, have been canceled, affecting initiatives like the iCET review.
- Strained Ambassadorial Ties: The absence of an Indian Ambassador in Washington and strained relations with the U.S. Ambassador in India have added tension.
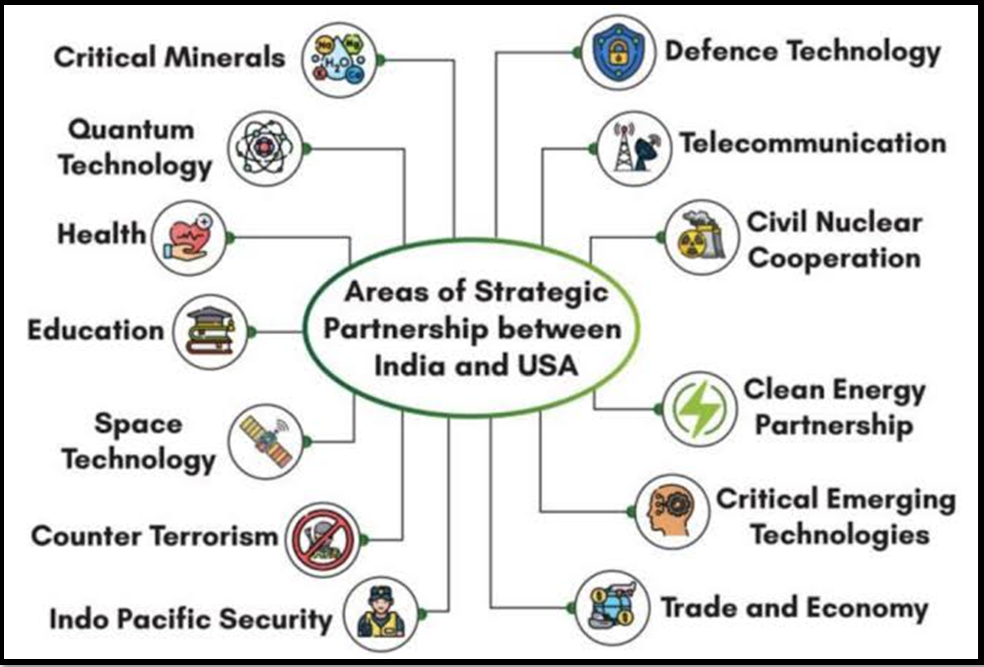
Initiatives of Cooperation Between India- USA
|
The China Factor
- Quad Cooperation Challenges: Logistics issues, such as President Biden declining an invitation to India’s Republic Day, have affected Quad cooperation.
- Cancelled Visits: Key visits by U.S. officials, such as NSA Jake Sullivan, have been cancelled due to crises like the Gaza conflict, impacting strategic reviews.
- Focus Shift: U.S. Deputy Secretary of State Kurt Campbell has focused on “Quad-Plus” meetings with other countries, diverting attention from India.
- Upcoming Quad Meeting: The Quad Foreign Ministers’ meeting in Japan depends on U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken’s availability, adding uncertainty.
- Human Rights Concerns: The U.S. State Department’s comments on human rights in India and other critical reports have strained diplomatic relations, leading to heightened sensitivity in New Delhi.
Tensions over Assassination Plots
- Khalistani Separatist Plot: The attempted assassination of U.S. citizen Gurpatwant Singh Pannun, allegedly by Indian security officials, has caused significant discomfort in the relationship.
- Canadian Citizen Incident: The killing of Canadian citizen Hardeep Singh Nijjar, linked to the plot, has further complicated matters.
- Broadening Concerns: Concerns over India’s actions have spread within U.S. intelligence, the Department of Justice, and Congress, affecting perceptions.
- Demand for Accountability: The U.S. demands for public accountability from India are unlikely to be met, but India must address the issue more transparently.
- Potential Impact on Relations: The ongoing trial in New York and subsequent developments in Canada could slow boil tensions, impacting diplomatic ties.
Future Prospects and Challenges
- Adjusting to New Realities: The Indian government needs to adjust to coalition realities post-election and engage effectively with the U.S. as it enters a “lame-duck” season.
- Potential Trump Presidency: A possible Trump presidency could resolve some issues but also introduce new uncertainties in India-U.S. relations.
- Critical Meetings: The opportunity for a Biden-Modi meeting and a follow-up visit by NSA Sullivan to complete the iCET review is crucial.
- Strategic Reset Needed: A strategic reset is required to regain the momentum lost over the past year and align bilateral goals.
- Focus on Long-Term Engagement: Both nations must focus on sustaining long-term engagement despite current challenges, ensuring that the relationship does not falter.
Way Forward: Strengthening India-U.S. Ties
- Enhance High-Level Engagements: Regular high-level meetings, such as the proposed India-USA summit and NSA Sullivan’s visit, should be prioritized to maintain momentum and address strategic concerns.
- Deepen Strategic Cooperation: Continue to expand cooperation in critical areas like defense, cybersecurity, and emerging technologies, ensuring both nations benefit from shared innovations and security enhancements.
- Resolve Diplomatic Strains: Address the absence of an Indian Ambassador in Washington and improve relations with the U.S. Ambassador in India to facilitate smoother diplomatic interactions.
- Clarify Human Rights Stances: Engage in transparent dialogues about human rights concerns to mitigate tensions and foster mutual understanding and respect for each country’s domestic issues.
- Strengthen Multilateral Cooperation: Align strategies on global conflicts, emphasizing shared principles while respecting each other’s historical and geopolitical contexts, to present a united front on the international stage.
- Boost Economic Ties: Focus on trade and investment, leveraging the U.S. as India’s top trading partner, and explore new opportunities for economic collaboration to drive mutual growth.
Conclusion
The past year has seen a mix of progress and setbacks in India-U.S. relations. While strategic and technological cooperation has grown, several internal and external factors have slowed the momentum. High-level engagements in the coming months are crucial to reset and strengthen the bilateral ties, addressing both longstanding and emerging challenges.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Evaluate the current state of India-U.S. relations, highlighting the achievements and challenges of the past year. Discuss the key areas that require attention to enhance bilateral cooperation and suggest measures to address these challenges effectively.
Associated Article: