Central counterparties or Clearing Corporation
Context: The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), the European Union (EU’s) financial markets regulator and supervisor, has derecognised six Indian central counterparties (CCPs)These six CCPs are The Clearing Corporation of India (CCIL), Indian Clearing Corporation Ltd (ICCL), NSE Clearing Ltd (NSCCL), Multi Commodity Exchange Clearing (MCXCCL), India International Clearing Corporation (IFSC) Ltd (IICC) and NSE IFSC Clearing Corporation Ltd (NICCL).
What is the issue?
- As per the European Market Infrastructure Regulations (EMIR), a CCP in a third country can provide clearing services to European banks only if it is recognised by ESMA.
- The decision to derecognise Indian CCPs came due to ‘no cooperation arrangements’ between ESMA and Indian regulators – the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA).
- While ESMA wants to supervise these six CCPs, Indian regulators are of the view that since these domestic CCPs operate in India and not in the EU, these entities cannot be subjected to the ESMA regulations. They feel that these six CCPs have robust risk management and there is no need for a foreign regulator to inspect them.
- Last year in December, Reserve Bank of India Governor Shaktikanta Das asserted that foreign regulators should trust the credibility of Indian regulations.
- In the Financial Stability Report, released in December 2022, the RBI said that after the global financial crisis of 2007-09, it is seen that the legislations governing financial market infrastructures (FMIs), like CCPs, enacted in some advanced jurisdictions have incorporated provisions that give them an extra-territorial reach.
- Such regulations, if implemented by all jurisdictions, can create a parallel maze of laws with overlapping requirements or restrictions and show a lack of trust in the capabilities and quality of oversight exercised by the host regulators,”
What will be the impact of the move?
- With the withdrawal of recognition, these TC-CCPs will no longer be able to provide services to clearing members and trading venues established in the EU, ESMA had said.
- Some of the major European banks dealing in the domestic forex, forward, swap and equities and commodities markets include Societe Generale, Deutsche Bank and BNP Paribas. The derecognition will impact these lenders and they will have to set aside additional capital to trade in the domestic market.
- The clearing members will also be impacted by way of higher capital requirements, increased margin requirements, enhanced credit risk and lack of multilateral netting benefit.
- However, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has said that the derecognition of these six CCPs is unlikely to have any impact.
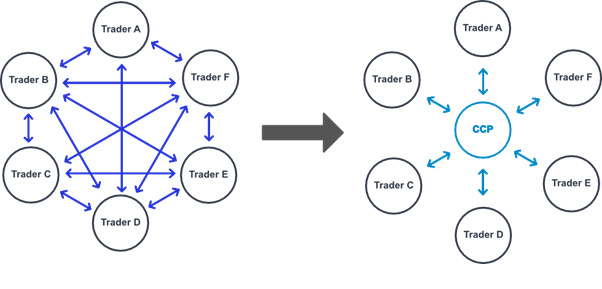
What’s the role of CCP?
- CCPs perform two main functions as the intermediary in a market transaction – clearing and settlement – and guarantee the terms of trade.
- CCP is a system provider, who by way of novation interposes between system participants in the transactions admitted for settlement, thereby becoming the buyer to every seller and the seller to every buyer, for the purpose of effecting settlement of their transactions.
- A CCP is authorised by the RBI to operate in India under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
| Practice Question
|