Birth certificate to be made mandatory for jobs, driving licence, passport, voting right
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Home Ministry proposed amendment to the Registration of Birth and Death (RBD) Act, 1969.
- The bill will be introduced in the winter session of parliament.
What are the Proposed Amendments?
- It has been proposed to make birth certificates a mandatory document for almost every sphere of life — admission in educational institutions, inclusion in the voter list, appointment in Central and State government jobs, issue of driving licence and passport.
- It shall be mandatory for hospitals and medical institutions to provide a copy of all death certificates, stating the cause of death, to the local registrar apart from the relative of the deceased.
- According to the Civil Registration System (CRS) report, the registration level of births for the country increased to 92.7% in 2019 from 82.0% in 2010 and that of registered deaths increased from 66.9% in 2010 to 92.0 % in 2019.
- CRS is an online system for registration of births and deaths under the operational control of the RGI.
What is the Need for the Amendments?
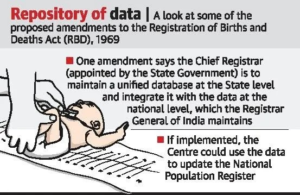
- The draft amendments would enable the Registrar General of India (RGI) under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) to “maintain a database of registered birth and deaths at the national level”.
- The birth and death database at the national level that will be available with the RGI may be used to update the Population Register, the Electoral Register, and the Aadhar, ration card, passport and driving licence databases.
- If the amendments are implemented, the Centre could use the data to update the National Population Register (NPR) that was first prepared in 2010 and revised through door-to-door enumeration in 2015.
- The NPR already has a database of 119 crore residents and under the Citizenship Rules, 2003, it is the first step towards the creation of a National Register of Citizens (NRC).
What is Registration of Birth and Death (RBD) Act, 1969?
- Registration of Births and Deaths in India is mandatory with the enactment of RBD, Act 1969 and is done as per the place of occurrence of the event.
- Under the RBD Act, it is the responsibility of the States to register births and deaths.
- State governments have set up facilities for registering births and deaths and keeping records.
- A Chief Registrar appointed in every State is the executive authority for implementation of the Act.
- A hierarchy of officials at the district and lower levels do the work.
- The RGI, appointed under this Act, is responsible for coordinating and unifying the implementation of the RBD Act.
What are the benefits of registration of birth and death?
The birth certificate is the first right of the child and it is the first step towards establishing its identity. The following compulsory uses of birth and death certificates are emerged:
- For admission to schools.
- As proof of age for employment.
- For proof of age at marriage.
- To establish parentage.
- To establish age for purpose of enrollment in Electoral Rolls.
- To establish age for insurance purposes.
- For registering in National Population Register (NPR).
- Compulsory production of death certificate for the purpose of inheritance of property and for claiming dues from insurance companies and other companies.
The database may be used to update the Population Register and the electoral register, and Aadhaar, ration card, passport and driving licence databases.