BHIMA RIVER
Why in the News?
- Due to the drying up of the Bhima River, around 100 villages, primarily in Indi taluk, are facing severe water scarcity.
- The region’s water bodies have also dried up, and disruptions in power supply are affecting water distribution.
The Issue
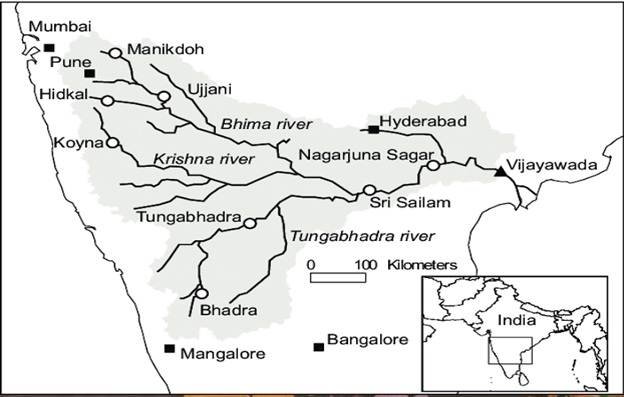
- The Bhima River, also known as Chandrabhaga River, originates in Maharashtra and flows through Karnataka, covering a distance of about 300 kilometers.
- For decades, the control of these rivers by Maharashtra has led to Karnataka’s dependency on its neighbour for water supply, particularly during the dry summer months.
- Maharashtra has at times demanded financial compensation from Karnataka to release water and has directed Karnataka to provide water to villages on the Maharashtra border.
- This situation has persisted since the reorganization of states in 1956, creating ongoing tensions regarding water sharing.
Origin and Path:
The Bhima River, a significant South Indian river, originates in the Bhimashankar hills of Maharashtra’s Pune district. It flows southeastward, passing through Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Telangana before merging with the Krishna River in Karnataka’s Raichur district.
Source: ResearchGate
Krishna River Tributary:
As an essential tributary of the Krishna River, the Bhima River holds importance for the region’s water network.
The Significance of the Bhima River:
- Spiritual Relevance: The Bhima River holds spiritual importance due to its association with the Bhimashankar Jyotirlinga temple and other religious sites, including the Vitthal Temple.
- Wildlife Habitat: It provides a habitat for unique wildlife species within the Bhimashankar Sanctuary, with the notable presence of the Giant Squirrel.
- Irrigation Facilities: The river contributes to practical irrigation, with dams such as Ujjani, Chas Kaman, and Mulshi constructed along its course to support agriculture and regional water needs.
Pollution Challenges:
- The Bhima River faces significant pollution challenges, with sewage, industrial effluents, and solid waste impacting approximately
- These issues are further exacerbated by high levels of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and coliform in the river’s.