AN AI INFUSED WORLD NEEDS MATCHING CYBERSECURITY
SYLLABUS:
- GS 2: Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, Nano-technology, bio-technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
Focus:
- Paris 2024 is getting ready to face an unprecedented challenge in terms of cybersecurity via AI.
Source: The motely
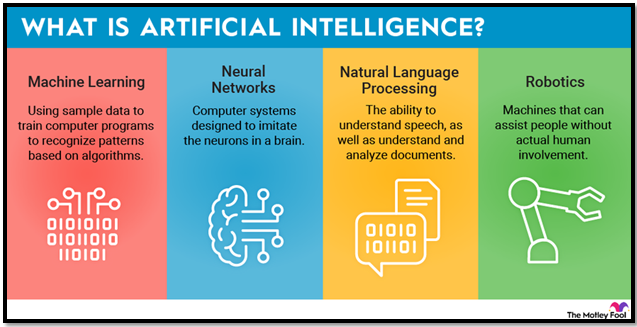
Overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Definition:
AI refers to the capability of computers or computer-controlled robots to perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. These tasks involve qualities such as reasoning, learning from experience, and making discerning choices.
Characteristics & Components:
- Rational Decision-Making: AI systems are designed to make rational decisions by selecting the most effective actions to achieve specific objectives.
- Machine Learning (ML): A critical component of AI, ML allows systems to learn from data patterns and improve over time without being explicitly programmed.
- Deep Learning (DL): This advanced subset of machine learning uses large amounts of unstructured data (text, images, videos) to learn and make informed decisions.
Advantages of AI:
- Accuracy and Precision: AI algorithms excel in processing large datasets with high accuracy, which is invaluable in fields like medical diagnostics and financial forecasting.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI helps identify trends and patterns that assist in making informed decisions.
- Innovation: AI drives technological and scientific advancements by discovering new insights and solutions across various domains.
- Productivity: AI enhances human capabilities, improving efficiency and output in numerous industries.
- Adaptability: AI systems continuously learn and adapt to new information and changing environments, maintaining relevance and effectiveness.
- Space Exploration: AI significantly contributes to space research, enabling autonomous vehicles and sophisticated data analysis in extreme conditions.
Disadvantages of AI:
- Job Displacement: Automation through AI can replace human roles, leading to unemployment and necessitating workforce retraining.
- Ethical and Privacy Concerns: AI introduces challenges such as potential bias in decision-making, privacy issues, and moral dilemmas in autonomous operations.
- Data Dependence: The effectiveness of AI is contingent on the availability and quality of data. Poor data can result in biased or incorrect outcomes.
- Security Vulnerabilities: AI systems are susceptible to cyber threats, with potential misuse by hackers to exploit or disrupt operations.
- Overreliance and Transparency Issues: Excessive dependence on AI without human oversight can lead to errors, especially in unfamiliar scenarios. Furthermore, some AI processes are not fully transparent, complicating the understanding of their decision-making pathways.
- High Costs: Initial and ongoing expenses for setting up and maintaining AI systems can be substantial, including investments in technology and continual updates.
An AI-Infused World Needs Matching Cybersecurity
Escalating Cyber Threats
- Increased Phishing and Credential Theft: There has been a significant rise in phishing incidents and credential phishing, with reported increases of 1,265% and 967% respectively since the fourth quarter of 2022.
- Use of AI in Cyber Attacks: Sophisticated AI technologies are being employed by cybercriminals to create more convincing scams and manipulations.
- Rise in Complex Cyber Threats: As AI technologies evolve, they open new avenues for cyber attacks, increasing the overall vulnerability of organizations and individuals.
- Challenges in Cybersecurity Detection: The evolving nature of AI-powered attacks makes them harder to detect, with many organizations reporting undetectable phishing attacks and an overall increase in attack volumes.
- Impact on Privacy and Security: The deployment of AI in areas like facial recognition and other biometric systems poses severe threats to privacy and personal security.
Strategic Responses Required
- Enhanced Collaboration for Cybersecurity: There is a need for greater collaboration among countries and corporations to develop effective cybersecurity measures.
- Development of Regulatory Frameworks: Implementing strict ethical and legislative measures to combat the misuse of AI in cybercrime is crucial.
- Promotion of Digital Literacy: Institutions should focus on enhancing digital literacy to help employees and the general public recognize and combat AI-driven threats.
- Consumer Protection Initiatives: The introduction of mechanisms like AI content watermarking can help consumers identify AI-generated content and avoid deception.
- Global Agreements on AI Safety: The signing of agreements like the Bletchley Declaration by global leaders emphasizes the importance of international cooperation in tackling the misuse of AI technologies.
Fostering Digital Awareness
- Corporate Training in Digital Literacy: Companies need to integrate digital literacy training into their routines to empower employees with the skills needed to navigate the digital landscape securely.
- Public Education Campaigns: Public education initiatives can play a pivotal role in building a digitally savvy citizenry that is well-equipped to face the challenges of an AI-driven world.
- Role of NGOs in Cyber Literacy: Non-governmental organizations are critical in introducing digital tools and cybersecurity awareness to the broader population.
- Creating a Holistic Cybersecurity Approach: It is essential to adopt a multi-faceted approach that includes feedback from all stakeholders to create effective and practical cybersecurity strategies.
- Empowering Communities Through Security: Continuous efforts to develop advanced security systems and technologies are necessary to maintain safety and security in the digital age.
| Current Global AI Governance
India:
United Kingdom:
United States:
China:
|
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
“Discuss the implications of artificial intelligence on cybersecurity. Analyze how AI can be both a boon and a bane in enhancing security measures and perpetuating cyber threats. Suggest measures that could be adopted at national and international levels to mitigate the risks posed by AI in cybersecurity.”
Associated Articles:
https://universalinstitutions.com/author/website-admin/page/134/