AFSPA Reimposed in Manipur to Tackle Unrest
Why in the news?
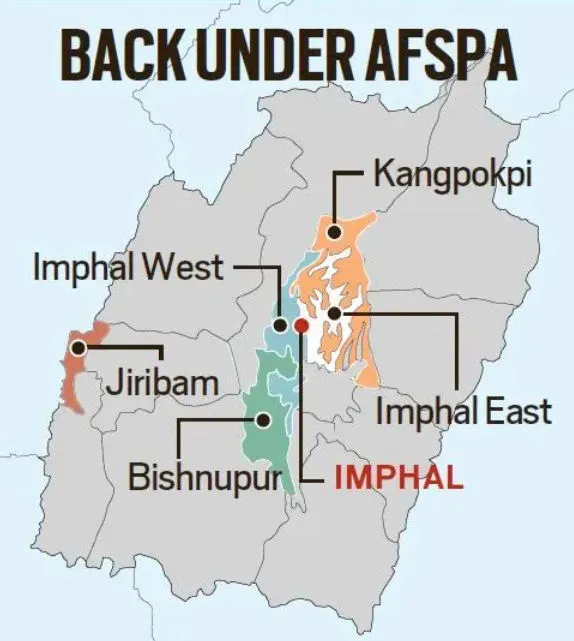
The Centre reinstated AFSPA in six police station areas of Manipur’s Imphal Valley, citing escalating violence and insurgent activity after its complete withdrawal in 2022.
Background and Context
- The Centre reinstated the Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) in six police station areas of Manipur on November 14, citing the volatile security situation and insurgent activities.
- AFSPA was fully withdrawn from these areas last year due to improved security. However, the recent resurgence of violence, including arson and attacks on politicians, has necessitated its return.
- Notably, six missing members of a Meitei family in Jiribam district were found dead in the Barak River, escalating tensions.
Understanding AFSPA and Its History in Manipur:
- Originating in 1958, AFSPA grants the military sweeping powers, including the authority to open fire, arrest without a warrant, and conduct searches on the basis of suspicion, with immunity from prosecution.
- AFSPA has a controversial history in Manipur, with allegations of excesses, including fake encounters and human rights violations.
- Initially imposed in Naga-dominated areas in 1958, it was later extended across the state, including the Meitei-dominated Imphal Valley, following the rise of insurgencies.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, 1958 (AFSPA):
- Background: Originated from British-era laws; enacted in 1958 to control “disturbed areas.” Extended to Northeast states like Nagaland, Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Provisions: Empower armed forces to open fire, arrest, and search without a warrant.
- Requires prior Central Government approval for prosecuting officers.
- States Covered: Parts of Nagaland, Assam, Manipur, and Arunachal Pradesh; repealed in Tripura (2015) and Meghalaya (2018).
- Controversial Provisions:
- Section 3: Declare areas “disturbed” without state consent.
- Section 4: Open fire/arrest/search without warrants.
- Section 7: Immunity to security forces.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times