A Voice of Gaza Under Occupation
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
- Tags: #Israel #Hamas #Palestine #GS2 #InternationalRelation #Gaza #war #currentaffairs #upsc
Why in the News?
Israel Hamas conflict has created a war like situation.
Mousa Abu Marzouk, a senior leader of Hamas, shared his views on the ongoing conflict in Gaza. He expressed frustration at the lack of progress in securing Palestinian rights. The following subheads summarize his perspective:
- Blocked Reconciliation: Abu Marzouk mentioned that Hamas attempted reconciliation but faced obstacles.
- Denied Elections: He noted that efforts to hold elections were thwarted.
- International Diplomacy: Despite seeking a political solution with the world’s involvement, he claimed little success.
- Frustration Over Peace: Abu Marzouk emphasized their desire for peace while asserting their rights.
- Lack of Progress: He pointed out the historical lack of progress towards the two-state solution.
Abu Marzouk highlighted a significant shift in the conflict
- Historical Perspective: He noted that Palestinians are now fighting in their historic land, contrasting with previous Israeli wars outside their borders.
- Shattering Invincibility: The conflict has challenged the perceived invincibility of one side.
Israeli Response to Hamas Attack
In response to the Hamas attack, Israel has taken several actions, which can be summarized as follows:
- Evacuation of Northern Gaza: Israel ordered the evacuation of the northern half of Gaza.
- Blockade: A blockade has been enforced, impacting the flow of goods, food, water, and electricity into Gaza.
- Military Presence: Israel has massed approximately 300,000 troops along Gaza’s border.
- Objective: The objective appears to involve occupying the northern zone and potentially expanding space for new settlements.
Historical Context and Palestinian Perspective
The Palestinians view these actions in light of their historical experiences, particularly the events surrounding the establishment of Israel in 1948. Many Palestinians see these actions as reminiscent of the displacement of Arabs in 1948.
- The Israeli leadership’s ideological stance is also a factor. Some Israeli leaders have equated Palestinians with Nazis and expressed a desire for their elimination. This echoes historical sentiments within right-wing Zionism.
- Despite numerous United Nations Security Council (UNSC) resolutions, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict has persisted, with resolutions remaining unimplemented. These resolutions have sought to address settlement activity and promote the two-state solution, but progress has been limited.
- The Abraham Accords, initiated in September 2020, aimed to address radicalization and conflict but have not led to significant changes in the conflict’s dynamics.
Questions to be asked
- Informed Arab columnists like Abdel Bari Atwan are of the opinion that the most recent fighting has deprived Israel of its two most effective weapons: its scariness and its deterrent power. Such a move, he says, would be more far reaching than Ehud Olmert’s foray and Ariel Sharon’s venture.
- The response of the United States and some of its allies to the present crisis raises the question of motivation. Did they know more about the chink in Israel’s armour? Did they apprehend the implications of conflict going beyond Gaza and its adverse impact on Israel?
Relevant Inquiries
Thomas L. Friedman’s analysis in The New York Times on October 16, 2023 raises several important questions regarding the situation:
- Post-Hamas Governance: If Israel were to remove Hamas from power in Gaza, who would take on the responsibility of governing Gaza
- Infrastructure Rebuilding: If Israel is involved in the destruction of Gaza’s infrastructure, will it commit to financing the reconstruction efforts, or would another entity handle this task?
- Humanitarian Crisis: What are Israel’s plans to address the unfolding humanitarian crisis in southern Gaza, and for how long will it permit this crisis to continue?
- Settlements and Borders: Is there an intention to establish new settlements in Gaza, and does Israel respect Gaza’s borders?
- Rebuilding Palestinian Authority: Does Israel have a plan to contribute to the reconstruction of the Palestinian Authority in the West Bank?
International Investigation Suggestion
Professor Anthony H. Cordesman of the Center for Strategic and International Studies recommends an international investigation led by credible nations or individuals to establish accountability, particularly regarding the recent hospital attack. Such an investigation could help clarify the situation.
As the world grapples with the intricacies of this enduring conflict, the urgency lies in fostering dialogue, seeking sustainable solutions, and avoiding actions that may exacerbate tensions or lead to further suffering. A comprehensive, inclusive, and fair approach, guided by genuine intentions for peace and stability for all parties involved, remains essential in reaching a lasting resolution to this enduring and deeply rooted conflict.
|
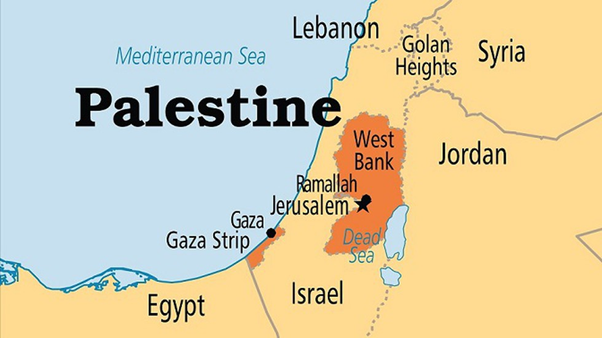
Gaza Strip
|
Mains Question
“Examine India’s diplomatic role in mediating the Israel-Hamas conflict. Discuss the challenges and opportunities in doing so, and evaluate the significance of India’s involvement in regional peace initiatives.