WTO HOBBLING WHEN THE WORLD NEEDS IT
Syllabus:
GS 2:
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
Focus:
- Recently, the 13th Ministerial Conference (MC13) of the World Trade Organization took place in Abu Dhabi, UAE.
Source:- WTO
The 13th Ministerial Conference of the World Trade Organization (WTO) in Abu Dhabi concluded with minimal achievements, highlighting the organization’s challenges in addressing global trade issues amid economic nationalism and geopolitical tensions. This article delves into the root causes of the WTO’s struggles, including the shift away from multilateralism, the crisis in its dispute settlement mechanism, development concerns, and the impact of trade protectionism.
Key Outcomes of WTO’s 13th Ministerial Conference:
- Accessions:
-
- Endorsed accession of Comoros and Timor-Leste, bringing WTO Membership to 166 countries, representing 98% of world trade.
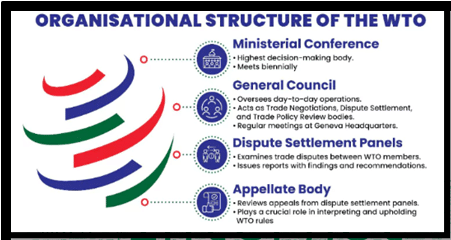
- Reform of Deliberative and Negotiating Functions:
- Welcomed efforts to improve WTO Councils, Committees, and Negotiating Groups.
- Emphasized enhancing organization’s efficiency and effectiveness.
- Committed to continue the reform process and report progress to MC14.
- Dispute Settlement Commitment:
- Renewed commitment to achieving a fully functional dispute settlement system accessible to all Members by 2024.
- E-Commerce Moratorium:
- Extended until MC14 or 31 March 2026, whichever is earlier.
- TRIPS Non-Violation and Situation Complaints:
- Extended moratorium on non-violation and situation complaints under the TRIPS Agreement.
- COVID-19-related TRIPS Waiver:
- Noted lack of consensus on expanding product scope for special rules, which won’t apply to Covid-19 diagnostics and therapeutics.
- Special and Differential Treatment:
- Adopted decision to improve the use of special and differential treatment provisions.
- Plurilateral Agreements and Initiatives:
- Several agreements or progress reports made in important areas, including Investment Facilitation for Development (IFD).
- Domestic Regulation of Services:
- Agreement reached on implementing new disciplines for domestic regulation of services, aimed at facilitating trade by streamlining procedures.
- Sustainability-Related Initiatives:
- Efforts made in sustainability initiatives, such as addressing plastics pollution and fossil fuel subsidy reform.
- Fisheries Subsidies:
- Progress welcomed towards the Agreement on Fisheries Subsidies (AFS) entry into force, with 71 Members ratifying as of March 1, 2024.
Challenges Currently Undermining the WTO’s Effectiveness:
- Erosion of Multilateralism:
-
- Noticeable decline in multilateral cooperation, leading to increased trade disputes and unilateral actions.
- Lack of progress in addressing key issues like fisheries subsidies during MC13 indicates serious divisions among member countries.
- Protectionism and Trade Wars:
- Proliferation of tariffs and trade barriers undermines principles of free trade.
- US-China trade dispute strains multilateral trading system and challenges WTO’s mediation capabilities.
- Dispute Settlement Mechanism Crisis:
- Dysfunction of WTO’s dispute settlement mechanism due to US blocking appointments to Appellate Body.
- Absence of functional mechanism erodes confidence in multilateral trading system.
- Development Divide and Special and Differential Treatment:
- Disparities persist in developing nations’ capacity to participate in trade negotiations and reforms.
- Least-developed countries lack resources and assistance, perpetuating their marginalization.
- Digital Trade and E-commerce:
- Rapid growth of digital trade poses regulatory challenges outside traditional trade agreements.
- WTO must adapt rules to accommodate digital trade while ensuring fair competition.
- Environmental and Sustainability Concerns:
- Pressure to incorporate environmental considerations into trade rules due to climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Balancing environmental objectives with trade liberalization requires innovative approaches.
- Public Health and Access to Medicines:
- Covid-19 highlights importance of public health in trade policy.
- Need to reconcile intellectual property rights with access to medicines, especially during emergencies.
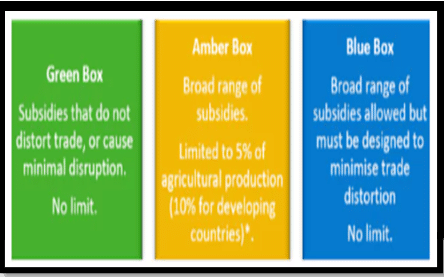
- Agriculture and Food Security:
- Little progress in updating WTO disciplines on agriculture since 2000.
- Failure to reach consensus at MC13, particularly on public stockholding for food security purposes, reflects ongoing challenges.
Key WTO Agreements: Shaping Global Trade Rules
|
The WTO is at a crossroads, challenged by economic nationalism, geopolitical tensions, and a departure from its foundational principles of multilateralism and consensus-based decision-making. To remain relevant and effective, the organization must overcome internal divisions, revive its dispute settlement mechanism, address developmental concerns meaningfully, and counter the rise of trade protectionism. Achieving these goals requires renewed political commitment from all member nations.
Source: India Express
Mains Practice Question:
“Examine the challenges faced by the World Trade Organization (WTO) in the context of the 13th Ministerial Conference outcomes. Discuss the implications of these challenges for global trade and suggest measures to rejuvenate the WTO for enhancing its role in promoting a fair and sustainable global trade system. Analyze the impact of economic nationalism and trade protectionism on the WTO’s functioning and its implications for developing countries.”