What is end-to-end encryption and why are tech companies focusing on it?
Why in the News?
Recently, Apple has announced it will be increasing the number of data points protected by End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) on iCloud from 14 to 23 categories.
What is End-to-End Encryption?
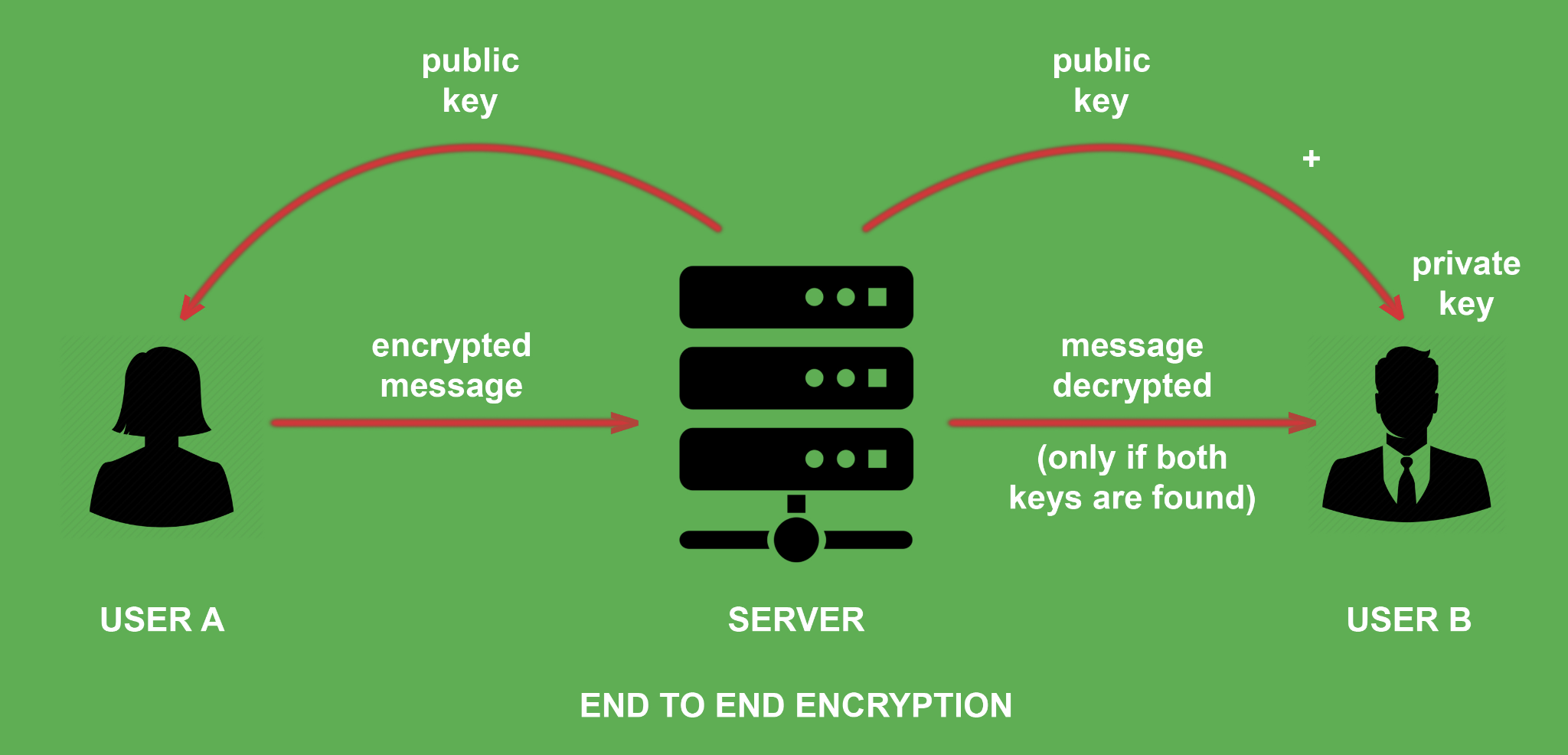
- End-to-end encryption is a communication process that encrypts data being shared between two devices.
- It prevents third parties like cloud service providers, internet service providers (ISPs) and cybercriminals from accessing data while it is being transferred.
- Mechanism:
- The endpoints hold the cryptographic keys that are used to encrypt and decrypt the messages.
- End-to-end encryption uses an algorithm to convert plain text into an unintelligible format.
- Exclusively individuals having the decryption keys, which are only kept on endpoints and not with any other parties like service providers, can decode and read this format.
- Usage:
- E2EE has long been used when transferring business documents, financial details, legal proceedings, and personal conversations.
- It can also be used to control users’ authorisation when accessing stored data.
- End-to-end encryption is used to secure communications.
- It is also used to secure passwords, protect stored data and safeguard data on cloud storage.
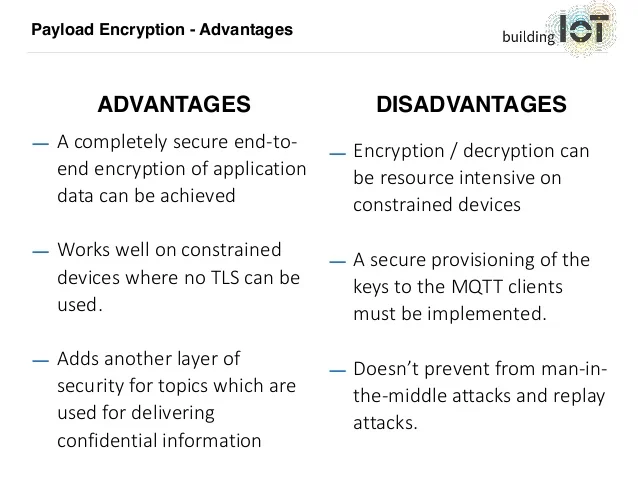
What are the Advantages of E2EE?
- Security in Transit
- Safety from Third Parties
- Tamper-Proof
- Compliance
What are the Disadvantages of E2EE?
- Complexity in Defining the Endpoints
- Too Much Privacy
- No Protection to Metadata
What is the Legal Framework for Encryption in India?
- Minimum Encryption Standards:
- There is no explicit encryption law in India. However, a number of industry regulations, including those that control the banking, finance, and telecommunications sectors, include demands for the use of minimal encryption standards in order to secure transactions.
- Prohibition on Encryption Technologies:
- According to the licencing agreement between the ISP and the DoT, users are not permitted to use encryption standards larger than 40 bits utilising symmetric key algorithms or comparable methods without prior clearance and deposition of decryption keys.
- There are numerous additional guidelines and laws that call for using an encryption level greater than 40 bits in specific areas.
- The Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021:
- The previous Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines) Rules 2011 were replaced by it.
- The end-to-end encryption methods used by social messaging apps like WhatsApp, Telegram, Signal, etc. may be affected by the new set of laws.
- Information Technology Act of 2000:
- It regulates electronic and wireless modes of communication, is devoid of any substantive provision or policy on encryption.