WHAT CAUSES INFLATION IN INDIA: DEMAND OR SUPPLY ISSUES?
Syllabus
- GS3: Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment.
Why in the News?
- The Reserve Bank of India’s December bulletin sheds light on the dynamics of inflation in India.
- It suggests that while supply-side factors primarily contribute to inflation, there are times when demand-side influences become significant.
Source: the Hindu
Inflation Dynamics in India
- Typically, inflation in India is chiefly influenced by supply-related factors, as highlighted in the Reserve Bank of India’s December bulletin.
Demand Factors in Focus
- The article notes that while supply disruptions were the main cause of inflation during the two COVID-19 waves, the dynamics shifted post the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Demand-related factors gained prominence in influencing inflation trends in India.
Pandemic’s Economic Impact
Lockdown-induced Decline
- The pandemic’s onset triggered significant production and demand declines, causing a sharp economic contraction.
- This phase witnessed reduced commodity prices due to weakened demand.
Uneven Recovery Post-Reopening
- Subsequent to economic reopening facilitated by vaccine distribution, demand rebounded faster than supply.
- This imbalance exerted upward pressure on commodity prices.
Russia-Ukraine Conflict Impact
- The 2022 Russia-Ukraine conflict intensified supply chain challenges.
- Compounding existing pressures on commodity prices, as highlighted in the Reserve Bank of India’s December bulletin.
Deciphering Inflation Drivers: Supply vs. Demand
Data Analysis Approach
- Utilizing consumer expenditure data from the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy, the article employs a methodical approach to discern whether inflation in India is propelled by supply-side or demand-side factors.
Demand-Driven Inflation
- The analysis identifies demand-driven inflation when there is an unforeseen simultaneous shift in prices and quantities, aligning in the same direction.
- Increased demand correlates with rising prices and quantities, while decreased demand corresponds to reductions in both.
Supply-Driven Inflation
- Conversely, inflation is classified as supply-driven when unexpected changes in prices and quantities move in opposite directions.
- Decreased supply is associated with lower volumes but increased prices, and vice versa.
Inflation Analysis (January 2019 – May 2023)
Supply-Side Constraints
- According to the applied methodology, categories like vegetables, oils and fats, milk, eggs, pulses, and sugar consistently face supply-side constraints, impacting their inflation dynamics.
Source: The hindu
Demand-Side Influences
- Conversely, items such as non-alcoholic beverages, personal care products, and health-related goods are predominantly influenced by demand-side factors, reflecting a distinct pattern in their Consumer Price Index (CPI) sub-group level inflation contributions.
Headline Inflation Analysis: Factors and Trends
Supply-Dominant Periods
- Analyzing CPI weights, the combination of demand and supply factors at the sub-group level provides insights into overall headline inflation trends.
- Supply factors predominantly drove inflation during specific periods: October 2019-January 2020 (excess rainfall causing disruptions), pandemic stages (related restrictions and supply chain challenges), and the early phase of the Russia-Ukraine conflict (supply shortages and global commodity price spikes).
Supply’s Average Contribution
- On average, supply-side factors constituted approximately 55% of CPI headline inflation from January 2019 to May 2023.
Source: The Hindu
- Chart 2 visually represents the monthly contribution of demand and supply to CPI inflation (excluding housing) during this period, highlighting the varying impacts of these factors over time.
Shifting Dynamics of Demand-side Impact
COVID-19 Crisis
- During the COVID-19 crisis, the influence of demand-side factors on headline inflation declined, plummeting from 41.5% in 2019 to 27.1% in 2020.
Intermittent Increases Post-COVID
- Despite the initial decrease, the relevance of demand-side factors intermittently increased post-COVID-19 waves and during the Russia-Ukraine conflict aftermath.
- Notably, these factors played a crucial role in the peak inflation observed in April 2022
Overall Contribution
- Across the entire January 2019 to May 2023 period, demand-driven factors contributed 31% to inflation, underscoring their enduring influence amid changing economic landscapes.
| Inflation
· Inflation is the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of currency. Demand-side Factors of Inflation Consumer Demand · When consumers demand more goods and services than the available supply, it can lead to increased prices. · For example, a surge in demand for electronic gadgets during the festive season. Government Spending · Government initiatives that boost spending, like increased infrastructure projects, can create a higher demand for resources, contributing to inflation. Investment Demand · If businesses increase investments, creating a demand for capital goods, it can lead to higher prices in that sector. Consumer Expectations · When consumers anticipate future price increases, they may buy more now, increasing current demand and causing inflation. Global Economic Conditions · External factors like changes in global economic conditions can impact demand. · For instance, a rise in oil prices globally can affect various industries. Supply-side Factors of Inflation Cost-push Inflation · An increase in production costs, such as higher wages or raw material prices, can lead to cost-push inflation. · For example, a surge in oil prices affecting transportation costs. Natural Disasters · Events like floods or droughts can disrupt the supply of agricultural goods, leading to shortages and increased prices. Government Regulations · Stringent regulations or taxes on production can constrain supply, resulting in inflation. · For instance, increased environmental regulations impacting manufacturing. Technological Disruptions · Rapid technological advancements can create supply shortages as industries adapt, affecting prices. |
Source :
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/inflation.asp
Mains Practice Question
Examine the factors influencing inflation in India, focusing on the interplay between demand and supply issues. Discuss the shift in the causes of inflation during the COVID-19 pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine conflict, emphasizing the role of supply disruptions and demand forces.

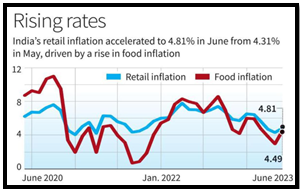 Source: the Hindu
Source: the Hindu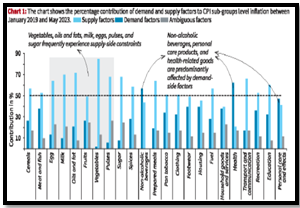 Source: The hindu
Source: The hindu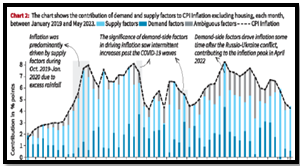 Source: The Hindu
Source: The Hindu

