Wayanad rice festival promotes climate-resilient crops
Why in the News?
Recently, a Kerala-based organisation, Thanal launched the Ikki Jathre or the Festival of Rice in tribal parlance whereby 300 climate-resilient varieties of traditional rice were planted at Panavally, Wayanad.
- Thanal initiated the Rice Diversity Block (RDB) at Panavally under the Save Our Rice campaign in 2009, with a collection of 30 varieties of rice which now expanded to 300.
What is Ikki Jathre?
- The campaign aims to raise awareness about the value of preserving indigenous crops that can resist extreme weather conditions.
- The event also creates a forum for tribal farmers and experts to collaborate on knowledge production and knowledge sharing.
- The majority of the varieties for the RDB were gathered in West Bengal, Kerala, Karnataka, Assam, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala.
- Three traditional rice varieties from Thailand and Vietnam are also available.
What is the Save Our Rice Campaign?
- About:
- Save our rice campaign is a people’s movement to protect the diverse rice cultures, knowledge, and ensure food sovereignty.
- In India, it started in 2004, and empowers communities to build sustainable food security and livelihood.
- Functions:
- The creation of community seed banks and RDBs, as well as the preservation and promotion of local paddy seed varieties.
- educating urban customers about the value of rice diversity.
- encouraging farmers, states, and local governments to use indigenous seeds, and facilitating the implementation of agro-ecological farming in rice habitats.
- enabling lively media debates regarding indigenous seeds and eco-friendly farming.
What are the Key Facts About Rice?
- Globally, two major varieties of rice are grown viz. Oryza sativa indicaand Oryza sativa japonica. Further, there are several varieties including wild rice, all of which make a so-called Oryza sativa complex.
- It’s a true grass and its edible part grain is its seed. The dehulled rice grain is covered by an outermost layer called pericarp and such rice with pericarp is called Brown rice. It is removed when rice undergoes milling and polishing.
- It’s a staple crop, rich in carbohydrates (Starch) and poor in protein / lipids. Brown rice is rich in some vitamins mainly Thiamine and B1.
- Rice straw is used as cattle feed, used for thatching roof and in cottage industry for preparation of hats, mats, ropes, sound absorbing, straw board and used as litter material.
- Rice husk is used as animal feed, for paper making and as fuel source.
- Rice bran is used in cattle and poultry feed, defatted bran, which is rich in protein, can be used in the preparation of biscuits and as cattle feed.
- Rice bran oil is used in the soap industry. Refined oil can be used as a cooling medium like cotton seed oil / corn oil.
- Rice bran wax, a byproduct of rice bran oil, is used in industries.
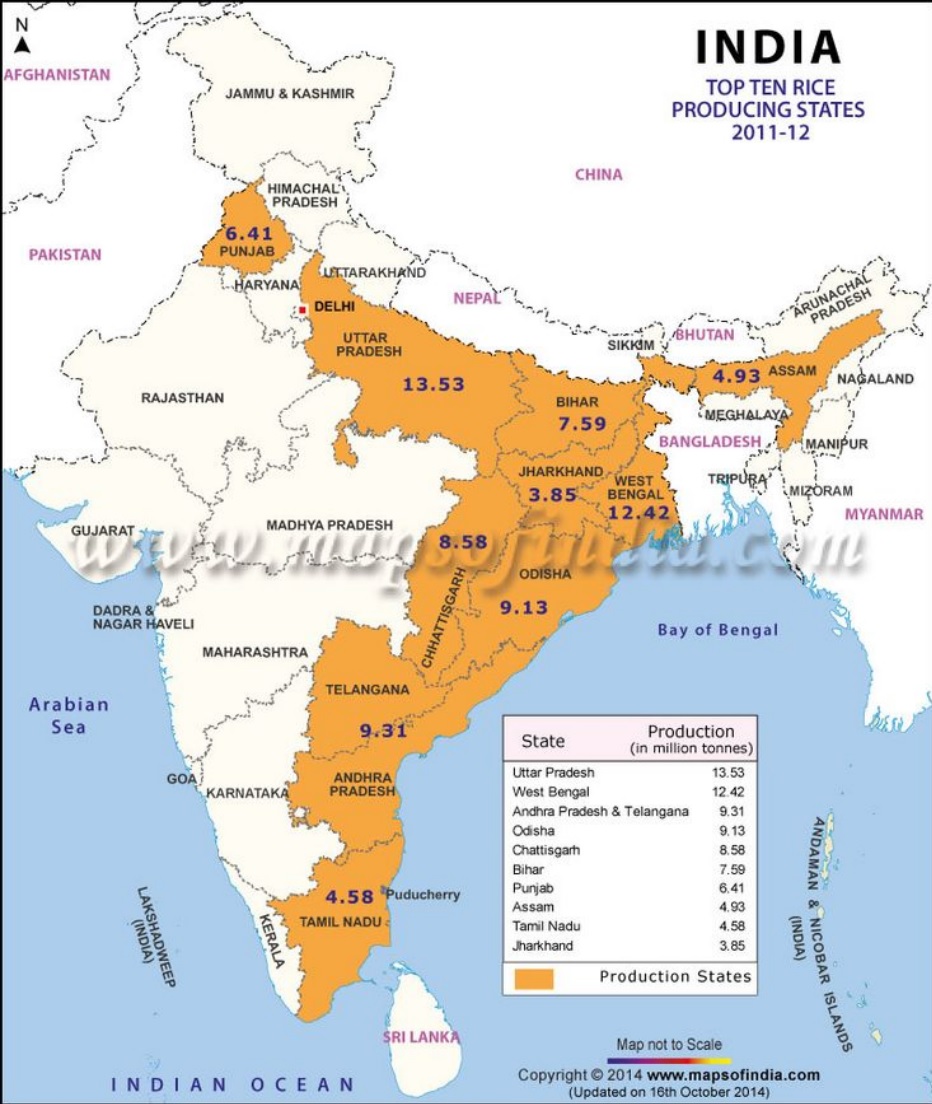
Production of Rice
- Top rice producing states are West Bengal and Uttar Pradesh. However, since it can be grown in all types of soil, almost all states of India have areas under rice cultivation.
- As per the fourth Advance Estimates for 2013-14, the production of rice in India is 106.5 million tonnes. Rice covers one third of the total cultivated area of India and provides food to more than half of the Indian population.
- This makes it India’s largest produced food crop both by area under cultivation as well as production.
- India is the second largest producer of rice after China; produces one fifth of the world’s rice; and is the largest exporter of rice.
- Rice is the staple crop in eastern and southern part of the country and is a very important crop in terms of national food security.
Cultivation of Rice
There are three seasons of rice growing viz. autumn, winter and summer.
- Autumn Rice is Pre-Kharif rice sown during May to August; and harvested in September-October. Autumn rice crop accounts for only 7-8% of total rice grown.
- Winter Rice is the Kharif rice in India, sown in June-July and harvested in November-December. This accounts for 84% rice cultivation in India.
- Summer rice is also called Rabi rice sown from November to February and harvesting time is March to June. This accounts for 8-9% of total rice cultivated in India.
- Thus, rice is predominantly a Kharif crop in India, grown in both irrigated areas as well as rain-fed areas with high rainfall. It requires hot and humid conditions for growing with 24° C mean temperature and 150-300 cm rainfall.
- The crop is predominantly labor oriented and is not much suitable for heavy farm mechanization.
- With regard to the soil, rice is grown both in uplands and lowlands. On this basis, there are several methods of rice growing such as Dry or Semi-dry upland cultivation; Broadcasting the seed; Sowing the seed behind the plough or drilling; Wet or lowland cultivation; Transplanting in puddled fields; Broadcasting sprouted seeds in puddled fields etc.