VIKSIT BHARAT MUST BE INCLUSIVE
Syllabus:
- GS-3:Indian economy and its related dimensions.
Focus :
- Vikshit Bharat envisions India’s transformation into a developed nation by 2047. In the context of agriculture, it aims to modernize the sector, enhance productivity, and ensure sustainable practices. By prioritizing agricultural growth, Vikshit Bharat seeks to achieve inclusive and balanced development, crucial for the nation’s overall progress.
Source- IE
Introduction to the Climate and Agricultural Challenges:
- 2023 recorded as the warmest year since 1850, with temperatures 18 degrees Celsius higher than pre-industrial levels.
- Concerns raised regarding the ability of Indian agriculture to sustainably feed the growing population amidst rising temperatures and climate uncertainties.
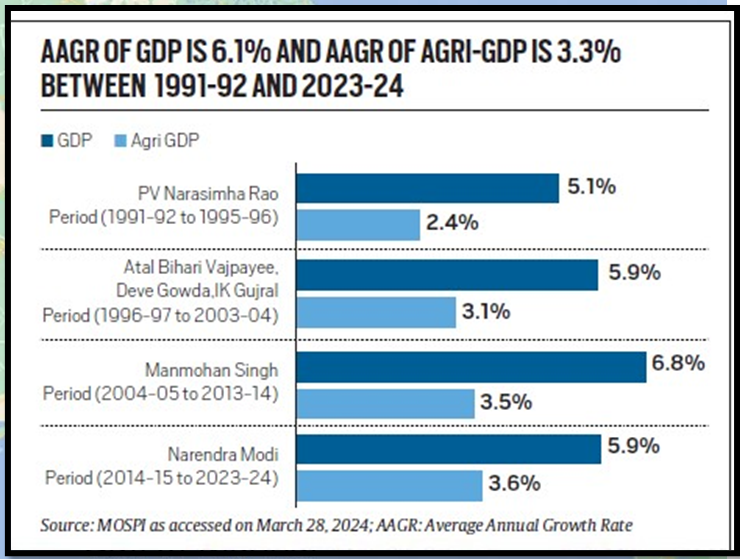
Evaluation of Agricultural Growth under Different Governments:
- Comparison between the agricultural growth rates during the tenures of the Narendra Modi and Manmohan Singh governments(Figure)
- Notable similarities observed in agricultural GDP growth rates despite different political regimes.
| About VIKSIT BHARAT :
· Vision Statement: The “Vikshit Bharat” strategy aims to transform India into a developed nation by 2047, coinciding with the centenary of its independence. · Inclusive Growth: The strategy prioritizes inclusive growth, ensuring that all sections of society benefit from economic development, with a focus on reducing income inequality and poverty. · Economic Diversification: It emphasizes economic diversification by promoting industries beyond agriculture, such as manufacturing, services, and technology, to create more job opportunities and boost GDP growth. · Infrastructure Development: Infrastructure development forms a crucial pillar of the strategy, with investments in roads, railways, ports, airports, and digital infrastructure to facilitate trade, connectivity, and efficiency. · Human Capital Development: The strategy prioritizes investments in education, healthcare, and skill development to enhance human capital, fostering innovation, productivity, and competitiveness. · Sustainable Development: Vikshit Bharat strategy integrates sustainability principles, aiming for environmentally sustainable growth through renewable energy adoption, conservation efforts, and climate change mitigation measures. · Global Engagement: The strategy emphasizes greater global engagement, promoting trade, investment, and international cooperation to leverage India’s position in the global economy. · Policy Reforms: It advocates for policy reforms across sectors, including governance, taxation, regulation, and ease of doing business, to create an enabling environment for entrepreneurship and investment. · Rural-Urban Integration: The strategy seeks to bridge the rural-urban divide by promoting integrated development, providing urban amenities in rural areas, and fostering balanced regional growth. · Resilience Building: Vikshit Bharat strategy emphasizes resilience building against future shocks and uncertainties, including pandemics, natural disasters, and geopolitical risks, through robust contingency planning and risk management mechanisms. |
Significance of Agriculture in India’s Development:
- Agriculture engages around 45% of the working population.Critical role of agriculture in ensuring inclusive development and achieving the vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
- Need for enhancing productivity, reducing water consumption, recharging groundwater, arresting soil degradation, and curbing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Business-as-usual approach insufficient to achieve inclusive growth in agriculture.
Projected Trends in Agricultural Contribution to GDP and Workforce:
- Potential decline in agriculture’s share in overall GDP to 7-8% by 2047.
- Persistence of a significant portion of the workforce in agriculture, posing challenges to inclusive development.
Importance of Skill Formation and Rural Development:
- Priority on skill formation for rural populations to transition to higher productivity jobs in an urbanizing India.
- Need for policies promoting skill development to ensure inclusive growth.
Current Economic Outlook and Agricultural Concerns:
- Positive overall GDP growth forecasted for 2023-24, with expectations of sustained growth.
- Contrastingly, agri-GDP growth remains low at 0.7%, raising concerns about the disparity in economic conditions.
Risks Associated with Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events:
- Vulnerability of Indian agriculture to extreme weather events due to climate change.
- Urgent need for adaptation measures to mitigate risks and ensure agricultural sustainability.
Agenda for Agriculture in Viksit Bharat:
- Rationalization of food and fertilizer subsidies to redirect funds towards agricultural research, innovation, and extension services.
- Investment in soil and water management through check dams and watersheds to enhance agricultural sustainability.
- Promotion of high-value agriculture focusing on poultry, fishery, dairy, fruits, and vegetables.
- Emphasis on value chain development and market access for farmers through cooperatives, FPOs, digital commerce, and contract farming.
- Advocacy for liberalizing futures trading to facilitate price discovery and market efficiency.
Conclusion:
- Need for proactive policies and investments to transform Indian agriculture into a resilient and sustainable sector capable of achieving the goals of Viksit Bharat.
Source:Indian Express
Mains Practice Question :
GS-3
“Discuss the challenges and prospects of Indian agriculture in achieving the vision of ‘Viksit Bharat’ by 2047, amidst rising temperatures, climate uncertainties, and evolving economic dynamics. Examine the role of government policies, technological interventions, and market reforms in ensuring inclusive growth, enhancing productivity, and mitigating risks associated with climate “(250 words)