Vehicle-to-Grid Technology: Powering India’s EV Future
Why in the News ?
The Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB) and IIT Bombay have launched a pilot project to explore Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology. This initiative aims to assess the potential of using electric vehicles as decentralized energy storage to support Kerala’s power grid.
V2G Adoption: Global and Indian Status
- Globally, countries like the UK, Netherlands, California (USA) encourage V2G by offering incentives for EV owners who supply energy back to the grid.
- In India, V2G is at an early development stage. Focus remains on EV charging infrastructure rather than energy return.
- The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) is working on guidelines for reverse charging, but regulatory and market structures need reform for V2G to thrive.
Kerala’s Initiative: KSEB-IIT Bombay Pilot Project
- Kerala faces rising evening peak demand due to fast-growing EV usage and rooftop solar expansion.
- The pilot will test EVs’ ability to stabilize the grid during peak hours, especially when solar energy isn’t available.
- The collaboration aims to explore cost-effective, eco-friendly solutions for grid resilience in India’s clean energy transition.
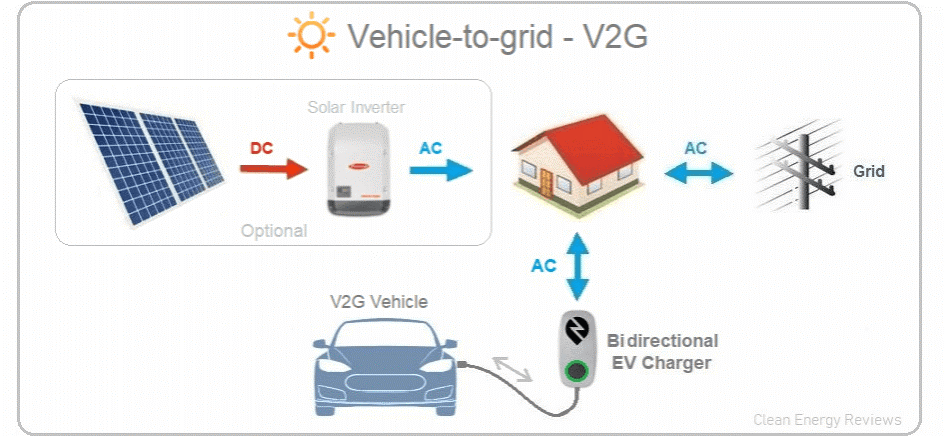
| What is Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology?
● V2G allows electric vehicles (EVs) to send unused power from their batteries back to the electricity grid. ● EVs can act as decentralized storage systems when parked and connected to bi-directional chargers. ● The technology supports the charging (Grid-to-Vehicle – G2V) and discharging (Vehicle-to-Grid – V2G) of EV batteries depending on grid demand. ● V2G can assist in renewable energy integration, offer demand response solutions, and enhance grid reliability. |