UTTARAKHAND TUNNEL COLLAPSE
Relevance:
GS 3
- Disaster and disaster management.
Why in News:
All the forty-one workers who were trapped inside Uttarakhand’s Silkyari tunnel since November 12 were evacuated safely.
Source- NDTV
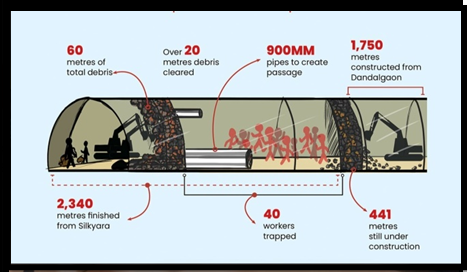
Silkyara Tunnel Accident
About Tunnel
- Length: The Silkyara Tunnel, designed to link Silkyara to Dandal gaon in Uttarkashi district, spans a total length of 4.5 km.
- Purpose: Part of the Char Dham all-weather road project, it is envisaged to shorten the journey from Uttarkashi to Yamunotri Dham by 26 kilometers.
- Sections Completed: 3 km of the tunnel has been successfully constructed from the Silkyara side.
- Work from Barkot End: Tunneling work from the Barkot end has reached a completion of 1.6 km.
- Pending Segment: Around 400 meters of the tunnel remains to be constructed to finalize the project.
Source- India Today
Agencies involved
- The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF), the State Disaster Relief Force (SDRF) and the police are among the main figures in the multi-agency rescue operations.
The Delayed Response
- The initial response to the collapse was hampered by logistical challenges and a lack of specialized equipment.
- It took nearly 24 hours for rescue teams to reach the trapped workers due to the remote location of the tunnel and the difficulty in accessing the collapse site.
- Communication with the trapped workers was limited, making it difficult to assess their condition and coordinate rescue efforts.
- The delayed response sparked widespread criticism and raised concerns about the adequacy of India’s disaster management capabilities.
Key Factors Contributing to the Delayed Response
- Inadequate infrastructure and lack of specialized equipment at the tunnel site
- Lack of clear communication channels and coordination among different agencies
- Insufficient training and preparedness for handling tunnel collapse scenarios
- Inadequate contingency plans and delayed decision-making
How were the workers rescued?
- Rescue team faced significant challenges in reaching the trapped workers due to the length and height of the tunnel.
- Initial attempts using advanced horizontal drilling techniques failed due to technical issues.
- Rescue team resorted to manual drilling for clearing the final 10 meters of debris.
- The team employed a combination of vertical drilling and rat-hole mining to bypass the obstruction and reach the trapped workers.
- Rat-hole mining is a contentious method due to the risks associated with miners working in confined spaces.
- The expertise and dedication of the rat-hole mining team played a crucial role in the successful rescue operation.
- The rescue operation highlights the importance of employing innovative techniques to overcome unforeseen challenges in disaster response.
- The team’s perseverance, adaptability, and willingness to embrace unconventional methods were instrumental in saving the lives of the trapped workers.
Moving Forward: Strengthening Disaster Management
The Silkyara tunnel tragedy serves as a wake-up call for India to strengthen its disaster management capabilities. Several key steps need to be taken to improve preparedness and response mechanisms:
- Invest in Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure: Prioritize the construction of infrastructure that can withstand natural disasters and adhere to strict construction standards.
- Enhance Early Warning Systems: Implement robust early warning systems to provide timely alerts for evacuation and minimize casualties.
- Empower Local Communities: Conduct regular disaster preparedness training and awareness campaigns to empower local communities to respond effectively in case of an emergency.
- Strengthen Inter-Agency Coordination: Establish clear communication channels and foster collaboration among different agencies for a coordinated response.
- Regular Drills and Simulations: Conduct regular drills and simulations to identify gaps in preparedness and improve response mechanisms.
- Allocate Adequate Resources: Ensure adequate funding and allocation of resources for effective disaster management.
- Prioritize Disaster Preparedness: Integrate disaster management into all aspects of development planning, from infrastructure projects to urban planning.
The Silkyara tunnel rescue operation stands as a testament to the unwavering determination and resilience of India’s rescue teams. Despite facing formidable challenges, the team persevered, employing innovative techniques and adapting to unforeseen obstacles to successfully rescue all 41 trapped workers. Their dedication and hard work deserve our utmost respect and admiration.
| Rat Hole Mining Overview:
· Rat-Hole: Refers to narrow pits dug into the ground, allowing manual extraction of coal either vertically or horizontally. · Method: Primitive tools like pickaxes and shovels are used for coal extraction from these rat holes. Types of Rat Hole Mining: · Side-Cutting: Involves digging narrow tunnels on hill slopes until reaching the coal seam. · Box-Cutting: Begins with a rectangular opening leading to a vertical pit dug from 100 to 400 feet deep. Ban and Prevalence: · Ban by NGT: National Green Tribunal banned rat hole mining in 2014 due to safety and scientific concerns. · Prevalence: Primarily used in Northeastern states, notably in Meghalaya, for extracting coal from narrow seams. Rat Hole Mining in Uttarakhand Rescue Operation: · Uttarakhand Incident: Tunnel collapse in Uttarakhand trapped 41 workers, prompting rescue efforts. · Technique Used: Rat hole miners entered rescue pipes, manually digging through debris to aid in the rescue operation. · Auger Machine Failure: Rat hole mining was employed after the failure of a 25-tonne auger machine. Concerns Associated: · Safety Hazards: Lack of regulation leads to unsafe conditions, causing accidents and fatalities among workers. · Environmental Impact: Rat hole mining contributes to land degradation, deforestation, and water pollution, posing significant environmental hazards. |
| Case study
1. Wangjialing Mine Rescue (2010): Chinese miners were trapped for over a week due to flooding in the Wangjialing coal mine in Shanxi, China. Rescuers worked around the clock to pump water out of the mine, successfully saving 115 miners. 2. Hatch and Portman Rescue (2021): In Yorkshire, UK, a father and son were trapped for over four hours in an old mineshaft. Rescue teams lowered a paramedic into the shaft to assess their condition before lifting them to safety. 3. Frejus tunnel collapse (2007): Seven workers were killed and 85 were injured when a section of a tunnel under construction in the French Alps collapsed. The rescue operation was complicated by the fact that the collapse had blocked access to the tunnel, and the rescuers had to work in a dark and confined space with the risk of further collapses. Despite these challenges, the rescuers were able to evacuate all of the injured workers within 24 hours. 4. Thai Cave Rescue (2018): Twelve Thai boys and their soccer coach were trapped for over two weeks in the Tham Luang Nang Non cave complex in Thailand. A multinational rescue operation involving divers and experts from various countries successfully evacuated them through the flooded cave passages. What India Can Learn · Swift Response: Rapid deployment of rescue teams and equipment immediately after the collapse played a pivotal role in the successful Wangjialing Mine Rescue. · Unified Command: A well-structured and coordinated command system among various rescue teams ensured efficient decision-making and resource allocation during the operation. · Innovative Technologies: Utilization of innovative techniques such as horizontal drilling and advanced capsule evacuation systems showcased the importance of technological advancements in complex rescue missions. · Effective Communication: Clear and consistent communication channels among rescue teams, authorities, and trapped miners facilitated smooth coordination, essential for the success of the operation. · Specialized Training: The expertise and training of the rescue personnel were instrumental in navigating the challenging mine conditions, underscoring the significance of continuous and specialized training for such emergencies. · Real-time Information: Ensuring real-time information sharing and updates aided in adapting strategies swiftly and making informed decisions throughout the rescue process. |
Source:
The Hindu, NDTV, India Today
Mains Question:
Q1. Critically analyse the factors that contributed to the Silkyara tunnel collapse and evaluate the effectiveness of the rescue operation. What is Rat hole mining?


 Source- India Today
Source- India Today

