US Fed Cuts Interest Rates to Boost Economic Growth
Why in the news?
- The US Federal Reserve (Fed) cut its benchmark interest rate by 50 basis points (0.5%) to boost economic activity.
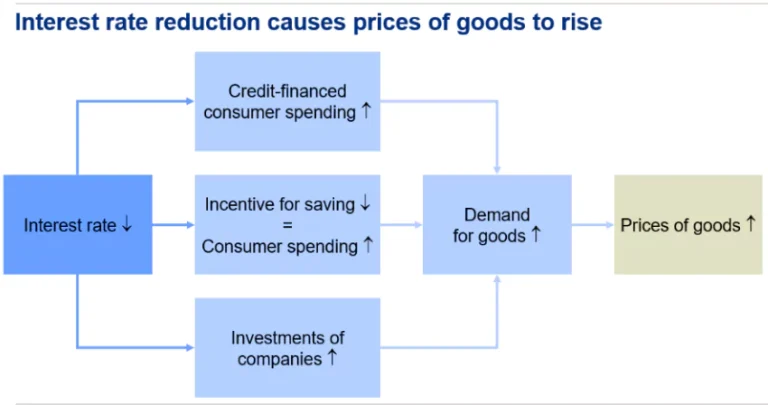
- Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper, encouraging growth and job creation.
- The Fed’s decision aims to achieve a “soft landing” by reducing inflation without triggering a recession.
Why the Fed Cut Rates:
- After aggressively raising rates to combat inflation post-COVID, the Fed maintained a5% rate for 15 months.
- Inflation has now moderated, nearing the Fed’s 2%
- Rising unemployment data pressured the Fed to shift focus from inflation control to boosting employment.
About US Federal Rate Changes:
- Federal Funds Rate: Primary monetary policy tool of the US Federal Reserve.
- Purpose: Influences employment and inflation by controlling credit availability and cost.
- Effects: Changes affect interest rates, influencing borrowing costs for households and businesses.
- Impact: Alters broader financial conditions, affecting consumer spending, investments, and overall economic growth.
- Authority: Set by the Federal Open Markets Committee (FOMC).
- Function: Guides overnight lending rates among U.S. banks, ensuring liquidity and stability in the banking system.
Federal Funds Rate:
- Definition: Interest rate set by the FOMC for overnight lending between banks.
- Purpose: Influences overall borrowing costs in the economy.
- Role: Key tool to manage inflation and employment.
US Fed Rate Cut:
- Definition: Reduction in the federal funds rate by the Federal Reserve.
- Impact: Lowers borrowing costs for banks, leading to lower loan interest rates for consumers and businesses.
Why the Fed Cuts Rates?
- Goals: Achieve price stability and maximum employment.
- Stimulus: Encourages borrowing, spending, and economic growth when unemployment rises or growth slows.
- The Fed is likely to cut rates further through 2024-2026.
Impact on India:
- Lower US interest rates may lead global investors to borrow in the US and invest in Indian markets (stocks, debt, FDI).
- A weakening US dollar may strengthen the Indian rupee, benefiting importers but negatively impacting exporters.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) may face pressure to adjust rates, but India’s inflation targets and economic needs differ significantly from the US.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times