Urgent Reform Needed for the International Monetary System
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 Important International Institutions, agencies and fora – their Structure, Mandate.
- Tags: #IMF #SDR #IMFReforms # International Monetary System #LivemintEditorial
Why in the News?
The international financial system is facing numerous challenges such as climate change, pandemics, conflicts, and economic disparities. To address these issues and enhance multilateral cooperation, reforming the International Monetary Fund (IMF) becomes imperative.
Global Economy in Crisis: Urgent Need for Multilateral Action
- The global economy faces a critical impasse due to climate change, environmental degradation, pandemics, mounting debt burdens, shifting demographics, and conflicts in regions like Ukraine, Africa, and the Middle East.
- These challenges disrupt the international financial system and deepen fragmentation.
- Meeting these requirements remains a challenge, even when considering the complete execution of decisions made at the recent IMF and World Bank meetings in Marrakech.
- This situation raises alarming risks, heightening concerns about global inequalities and severe shortages.
- Immediate major international initiatives are imperative, alongside efforts to revive multilateral cooperation, to tackle these pressing issues and safeguard the world from nearing crises.
Revamping the IMF for Global Stability
- To make the global financial system work better, reforming the international monetary system is crucial.
- While efforts like the Palais Royal Initiative have been made since the Global Financial Crisis, progress has been slow.
- Even if immediate changes are difficult due to the current political climate, we must get ready for necessary reforms.
Three key pillars for revamping the IMF, a major player in this system, are:
- Fairness: The IMF should operate more fairly.
- Updated Mandate: Its role should adapt to the demands of the 21st century.
- Global Governance: It needs to play a stronger role in managing the global monetary and financial governance.
First – Promoting Fairness
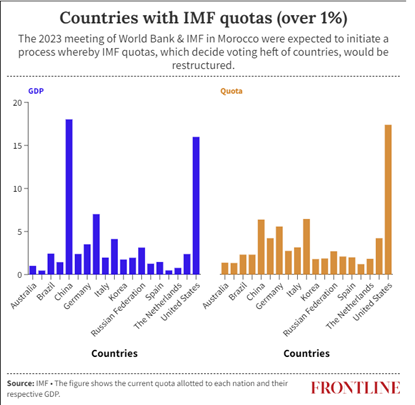
IMF Quota Reforms
- One critical aspect of reforming the international monetary system is to ensure fairness.
- This starts with reviewing the quotas of member countries within the IMF.
- IMF quotas, which determine a country’s financial contribution and voting power, need an update.
- They should reflect the actual economic standing of each member country.
- For instance, China and other emerging nations currently have disproportionately smaller quotas compared to the US and other industrialized countries.
Restructuring the Board of Directors
- The composition of the IMF’s Board of Directors also needs a fairness makeover.
- Important decisions require an 85% majority, effectively giving the US veto power.
- This dominance should be reduced, as unanimously proposed by the Palais Royal Initiative, which included notable figures like former US Federal Reserve chairman Paul Volcker.
Equitable Distribution of Special Drawing Rights (SDR)
- To ensure fairness, the distribution of Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) needs a rethinking.
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) are a sort of global currency issued by the IMF under specific conditions.
- The latest $650 billion allocation in 2021 followed the same quota-based system, benefiting wealthier nations more.
- As a positive step, the IMF urged affluent countries to donate some SDRs to the poorest nations via IMF Trust Funds.
- A fairer approach could involve dedicating approximately 20% of future SDR allocations specifically to the world’s neediest countries.
Balanced IMF Surveillance
- IMF’s oversight of its member countries should also focus on fairness.
- Currently, it leans heavily towards countries seeking financial help while others with external payment surpluses or significant global influence often disregard its recommendations.
- A more balanced approach is necessary.
- The focus of this oversight should also extend to countries’ external reserves, which sometimes far exceed reasonable levels.
- Some nations lock up a substantial part of global savings in short-term investment, limiting funds for crucial long-term projects like environmental initiatives, impacting our collective ability for sustainable progress.
Second – Expanding IMF’s Mandate for Global Stability
Surveillance of Capital Flows
- The IMF’s mission should explicitly encompass monitoring capital flows, which have a bigger impact on exchange rates and economies than current account balances in today’s financial world.
Global Liquidity Management
- Collaboration with the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and leading central banks is essential to create a framework for managing global liquidity.
- The goal is to prevent financial crises and keep the global financial system intact.
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) could be used to balance liquidity shortages or surpluses, essentially transforming the IMF into a global central bank.
- To make SDRs more effective in managing global liquidity, steps must be taken to broaden the SDR market and strengthen its status as a global currency.
Lender-of-Last-Resort Role
- The IMF’s role as a lender of last resort should be more explicitly stated in its Articles of Agreement, with a substantial increase in its resources.
- This ensures that countries facing unpredictable financial swings have a safety net, reducing the need for them to stockpile excessive and unproductive reserves.
Third – Enhancing IMF Governance for Inclusivity
Strengthening the IMFC Role
- To boost the IMF’s democratic accountability and credibility, the International Monetary and Financial Committee (IMFC), composed of finance ministers and central bank governors from 24 Executive Board countries, should play a more influential decision-making role.
- Executive directors, tasked with administrative responsibilities, should prepare the agenda, enhancing the IMFC’s decision-making authority.
G20 Representation Review
- Considering the G20’s expanded role in reshaping global financial institutions, it’s crucial to reassess its composition.
- A review aimed at achieving fair and inclusive representation for all nations in global strategies should adopt a system of regional constituencies, similar to the Bretton Woods institutions.
- Progress in this direction occurred during India’s G20 presidency, aligning with this objective.
The proposed reforms would make the IMF more democratic and universally inclusive. With these changes, the IMF can effectively fulfill its responsibilities, effectively reshaping the international financial system.
|
What is the IMF?
Foundation of the IMF
IMF’s Key Missions The IMF has 3 crucial missions
IMF’s Functions
|
Source: Livemint
Mains Question
Discuss the need for reforming the international monetary system, focusing on the role of the IMF. Highlight the challenges and the significance of creating a more equitable global financial order.