UPSC Essentials: India, Nepal agree to take forward Sapta Kosi high dam project
Why in News?
Recently, India and Nepal have agreed to take forward the Sapta Kosi high dam project through further studies.
- Senior officials of the two sides have met and reviewed the bilateral water-sector cooperation, including the implementation of the Mahakali Treaty.
Key Highlights:
Sapta Kosi High Dam Project & Mahakali Treaty:
- Sapta Kosi High Dam Project:
Sapta Kosi High Dam Project
-
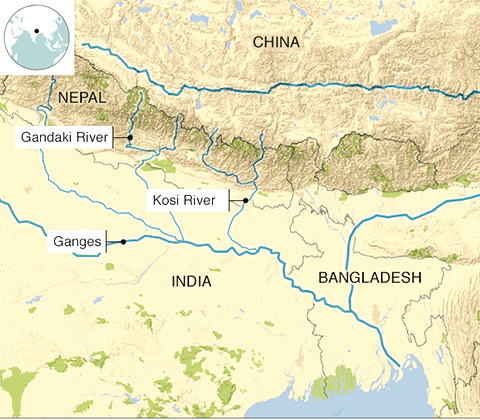
- Sapta Kosi High Dam is a multipurpose project proposed to be constructed on the Saptakoshi River of Nepal (Known as Kosi River in India).
- The project is primarily aimed to control floods in south-east Nepal and northern Bihar and to generate hydropower.
- The project will provide irrigation, control floods and generate 3,000 MW of electricity.
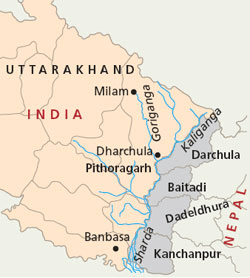
- Mahakali Treaty:
Mahakali Treaty
-
- The Mahakali Treaty was signed in 1996 over the integrated development of the Mahakali River, including Sarada Barrage, Tanakpur Barrage and Pancheshwar project.
- Mahakali River is also known as Sharda River or Kali Ganga in Uttarakhand.
- It joins Ghagra river in Uttar Pradesh, which is a tributary of Ganga.
Kosi River System:
- The Kosi is a transboundary river that flows through Tibet, Nepal and India.
- It has its source in Tibet that includes the world’s highest upland, it then drains a large part of Nepal before emerging onto the Gangetic plains.
- Its three major tributaries: the Sun Kosi, Arun and Tamur meet at one point just upstream of a 10 km gorge cut through the Himalayan foothills.
- The river crosses into northern Bihar, India where it branches into distributaries before joining the Ganges near Kursela in Katihar district.
- The Kosi carries the maximum amount of silt and sand after the Brahmaputra in India.
- It is also known as the “Sorrow of Bihar” as the annual floods affect about 21,000 sq. km. of fertile agricultural lands thereby disturbing the rural economy.
Recent Developments in India-Nepal Relations:
- Build Own Operate and Transfer (BOOT):
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the Government of Nepal and Sutlej Jal Vikas Nigam (SJVN) Limited for the project in 2008 for execution on a Build Own Operate and Transfer (BOOT) basis for a period of 30 years including five years of the construction period.
- Hydropower Projects:
- Nepal also invited Indian companies to invest in the West Seti hydropower project in Nepal.
- Cross-border Rail Link:
- The operationalisation of the 35 kilometers cross-border rail link from Jayanagar (Bihar) to Kurtha (Nepal) will be further extended to Bijalpura (Nepal) and Bardibas (Nepal).
Source:TOI






