Unemployment
Unemployment
The theoretical definition of unemployment according to the oxford dictionary states that Unemployment is a situation when a person is searching for employment, is unable to find work, whereas the abstract definition can be well elucidated by the approx. 200 million unemployed people across the globe. High persistence unemployment can signal serious distress in an economy and can even lead to social and political upheaval.
Types of Unemployment
DISGUISED UNEMPLOYMENT
- It is a phenomenon where more people are employed than actually
- It is commonly seen in agriculture – backed countries such as India, Liberia, China, where the marginal productivity of additional laborers is
- It’s predicted that even if 10-20% of agricultural laborers shift themselves from the primary sector to other sectors of the economy, the agricultural contribution to Indian GDP would remain the same.
STRUCTURAL UNEMPLOYMENT
- Category of unemployment arising from the mismatch between jobs available in the market and the skills available.
- A study showed that the Unemployment of graduates and post-graduate has increased faster than among matriculates, which means, on one hand, there is unemployment among the technically qualified people and on another hand, there is a lack of technical skills required for economic growth.
SEASONAL UNEMPLOYMENT
- It happens when people don’t have work during certain seasons of the
- Usually faced by Agricultural laborers, where work is available during busy seasons such as sowing, harvesting, weeding, and threshing but they remain unemployed during the other months of the.
VULNERABLE UNEMPLOYMENT
- This refers to the unemployment to the unemployment, where people are employed but informally i.e. without proper job contracts and thus records of their work are never maintained.
- According to the World Bank (Derived from ILO Data) 3 out of 4, that is 77% of total workers in India fall under vulnerable
- The government has introduced various Acts such as the Code on Social Security act – 2020 to bring unorganized sector, gig workers, and platform workers under the ambit of social security schemes.
TECHNOLOGICAL UNEMPLOYMENT
- It is a situation when people lose their jobs due to advancement in
- According to analysis firm ‘Oxford economics’, Up to 20 million manufacturing jobs would be replaced by robots by
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is well planned even to replace the service
- E.g.
- Technometrics – Singapore based Robotics Company that has developed robots targeted exactly at the hospitality and health-care industry.
- Brigo Coffea – Texas-based robotic company developed a robot that prepares coffee with accuracy and precision and also serves its
CYCLICAL UNEMPLOYMENT
- It is a result of business cycles when unemployment rises during the recession and declines with economic
- E.g.
- In 2008 and 2009, unemployment rose sharply as GDP contracted in the U.S as it was under recession from December 2007 to June
- The initial spike in unemployment in 2020 due to COVID-19 represents jobs lost directly from negative economic shock and not the normal cyclical
Unemployment due to COVID-19 impact
INDIA: Report by ILO and ADB
- As many as 41 lakh youths in the country lost jobs due to the COVID-19 pandemic so
- Construction and farm sector workers accounted for the majority of job losses
Impact on the world
- The world lost nearly 400 million full-time jobs in Q2 Financial year due to COVID-19. According to the data compiled by
- 59% of full-time jobs have been wiped out in Asia-Pacific
- South Asia accounted for 110 million job losses out of the total 235 million full-time jobs with an increase of over 400%.
- Arab countries accounted for 8 million job losses with a 300% increase in
- Americans lost over 70 million full-time jobs due to the pandemic with 536% fold
- Africa incurred serious job devastation of 45 million in Q2 of
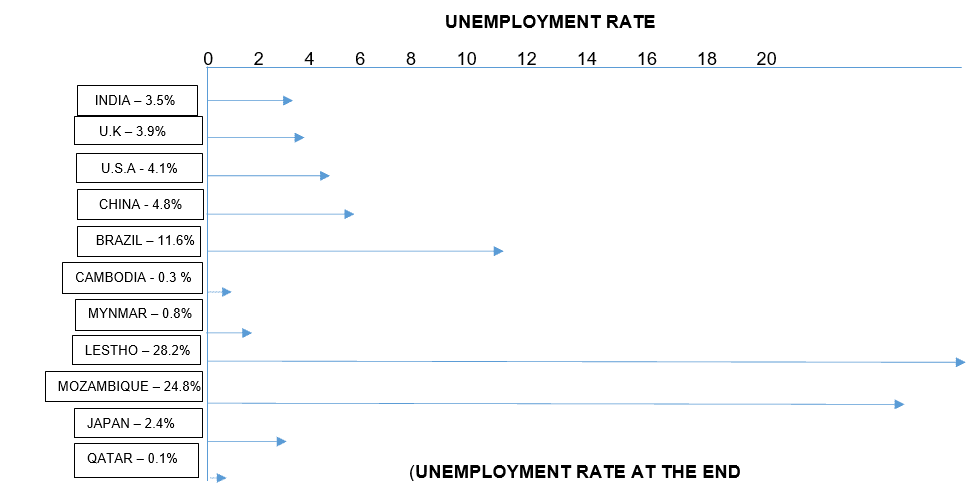
Global comparison of the unemployment rate
- The unemployment rate refers to the percentage of unemployed workers in the total labor force.
THE WAY FORWARD
- Public investment in sectors like health education, police, and the judiciary.
- Decentralization of Industrial
- Development of Rural
- Encouraging entrepreneurship among
- Removing social barriers for women’s
- Strict watch on Education
- Enhancing human capital through Skill
- Use of labor-intensive
- Implementation of National Employment
- Supporting the private sector to become a major investor in productive
- Promoting Self Reliance India (Aatmanirbhar Bharat).
More Government policies such as;
- Integrated Rural Development Programme –
- Training of Rural Youth for Self-Employment.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MNREGA) –
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) –
- Startup India Scheme – 2016
- Standup India Scheme – 2016