UNDERSTANDING POTASSIUM CYANIDE POISONING
Focus:
Potassium cyanide is making headlines due to its deadly effects on the human body:
- It disrupts oxygen transport in cells by binding to hemoglobin and cytochrome, crucial proteins for respiration.
- This deprivation causes rapid and severe health deterioration, leading to fatal consequences if untreated.
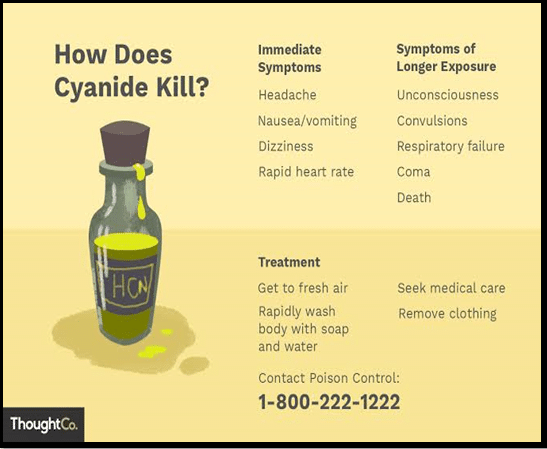
Source: thoughtco
How Does Potassium Cyanide Cause Sudden Death?
Mechanism of Action:
- Interaction with Haemoglobin: Cyanide ions replace oxygen-binding sites on haemoglobin, halting oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Impact on Cytochrome-a: Specific cytochrome variants like cytochrome-a also become disabled by cyanide, disrupting cellular oxygen utilization.
Signs of Poisoning:
- Initial symptoms include dizziness, headaches, and cyanosis (bluish skin coloration).
- Without prompt medical intervention, cyanide poisoning progresses to unconsciousness and ultimately death due to oxygen starvation
| Key Terms:
Haemoglobin: Haemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body. It consists of globular protein and heme groups, each containing iron that binds oxygen for delivery to cells. Cytochrome-a: Cytochrome-a is a type of cytochrome, a protein involved in cellular respiration. It plays a critical role in transferring electrons in the electron transport chain, facilitating the production of ATP and energy within cells. |