UK Cedes Chagos Sovereignty, Retains Diego Garcia Base
UK Cedes Chagos Sovereignty, Retains Diego Garcia Base
Why in the News ?
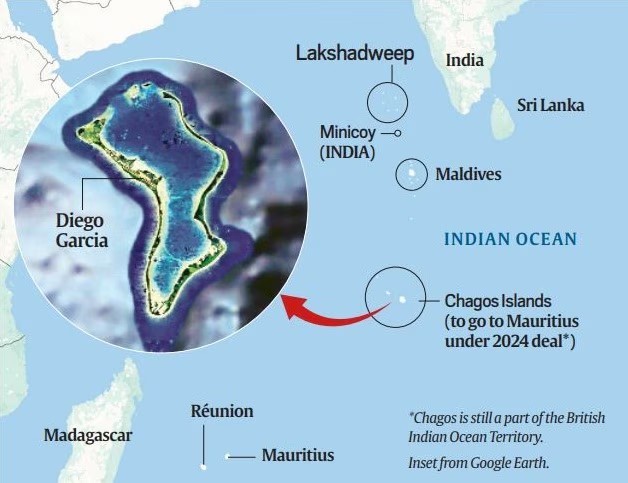
The UK and Mauritius signed a historic deal returning sovereignty of the Chagos Archipelago to Mauritius, while the UK retains control over the Diego Garcia military base under a 99-year lease. India welcomed this as a milestone for decolonization. The agreement has significant implications for the Indian Ocean region and global strategic interests, particularly concerning the status of Diego Garcia, which belongs to the British Indian Ocean Territory.
Highlights of the Deal and Strategic Significance:
- The UK signed an agreement with Mauritius to return sovereignty of the Chagos Islands, ending over 50 years of British control over the British Indian Ocean Territory.
- The deal was signed after a UK court lifted a last-minute injunction filed by a British-Chagossian group.
- Diego Garcia, the largest island in the Chagos Archipelago, will remain under UK control under a 99-year lease to ensure security of the US-UK joint military base. The question of which country Diego Garcia belongs to remains complex, given its strategic importance and the recent sovereignty transfer.
- The base’s location in the Indian Ocean is of critical strategic value, aiding operations in Iraq, Afghanistan, the Red Sea, and the Indo-Pacific. It serves as a key refueling point and hosts important military facilities. This strategic importance makes Diego Garcia a crucial topic for UPSC aspirants studying international relations, making “Diego Garcia UPSC” a relevant search term for exam preparation.
Global and Regional Reactions
- UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer said the deal ensures protection from malign influences and secures long-term strategic interests in the Indian Ocean region.
- US Secretary of State Marco Rubio welcomed the agreement for maintaining the effective operation of the Diego Garcia base, which is crucial for US-UK agreement on military cooperation.
- The deal was delayed previously due to leadership changes in Mauritius and the Trump administration’s transition.
India’s Support and Decolonization Stand
- The MEA called the agreement a “milestone achievement”, praising the peaceful resolution of a colonial dispute over the Chagos Archipelago.
- India reiterated support for Mauritius’s legitimate claim over Chagos, aligning with India’s stand on decolonization and respect for sovereignty.
- Mauritius PM Navin Ramgoolam hailed the deal as the completion of decolonization and recognition of Mauritian sovereignty over the British Indian Ocean Territory.
Chagos Archipelago and Diego Garcia – Key Facts |
| ● Location: Chagos Archipelago lies 500 km south of Maldives in the Indian Ocean; it comprises 58 islands. |
| ● Colonial History: France ceded Chagos to Britain in 1814; Britain separated it from Mauritius in 1965 to form BIOT. |
| ● Displacement: Chagossians were forcibly displaced in the 1960s–70s for a US military base on Diego Garcia. |
| ● Strategic Base: Diego Garcia, leased in 1967, became a base in 1986; used in the Gulf, Iraq, Afghanistan wars. |
| ● Recent Update: In 2024, UK agreed to cede sovereignty to Mauritius (post ICJ 2019 ruling) but retained Diego Garcia on a 99-year lease. |
Diego Garcia’s Strategic Importance
The Diego Garcia island plays a crucial role in global military strategy:
- It serves as a vital naval communications station in the Indian Ocean.
- The island hosts significant military facilities, including an airfield capable of handling large aircraft.
- Its location allows for power projection across the Indian Ocean and into the South China Sea.
- The base supports operations of nuclear submarines and aircraft carriers.
- Diego Garcia’s strategic location near key maritime chokepoints enhances its value for global naval operations.
Environmental and Sovereignty Concerns
While Diego Garcia’s strategic importance is clear, several issues persist:
- The ongoing Mauritius claim to the island challenges UK sovereignty, raising the question of which country Diego Garcia belongs to.
- Environmental risks include potential fuel spills and the impact of coral mining.
- The presence of invasive species threatens the island’s ecosystem.
- United Nations resolutions have called for the complete decolonization of the Chagos Archipelago.
- The base’s expansion raises concerns about increased environmental risks in the fragile Indian Ocean ecosystem.
Future Outlook
As lease negotiations continue, several factors will shape Diego Garcia’s future:
- The need to balance strategic importance with environmental protection.
- Addressing the rights and concerns of displaced Chagossians.
- Navigating the geopolitical implications of China’s expansion in the Indian Ocean.
- Ensuring the base continues to support global maritime security efforts.
- Balancing US-UK agreement terms with international pressure for decolonization.
The fate of Diego Garcia remains a complex issue, intertwining military strategy, sovereignty claims, and environmental concerns in the heart of the Indian Ocean. The question of which country Diego Garcia belongs to continues to be a point of international debate, with implications for regional stability and global geopolitics.
While Diego Garcia tourism is currently restricted due to its military status, there is ongoing discussion about the potential for limited civilian access in the future, balancing security concerns with the island’s unique ecological and historical significance.
As the capital of the British Indian Ocean Territory, Diego Garcia plays a pivotal role in regional politics and international relations. Its status as an island in the Indian Ocean makes it a key strategic asset, influencing maritime policies and security arrangements across the region. For those interested in understanding the geographical context, a Diego Garcia map would show its strategic position in the central Indian Ocean, highlighting its importance for naval operations and regional influence.