TWIN PEAKS : FROM GANDHI’S CHARKHA TO MODI’S CHIP
Syllabus:
- GS 3 : Growth and development , Indigenization of technology.
Focus:
- Mahatma Gandhi’s charkha, a symbol of India’s struggle for political independence and self-reliance, laid the foundation for the swadeshi movement.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s recent initiatives in semiconductor manufacturing mark a significant shift towards technological self-sufficiency, reflecting India’s evolution from handspun cloth to cutting-edge chip technology.
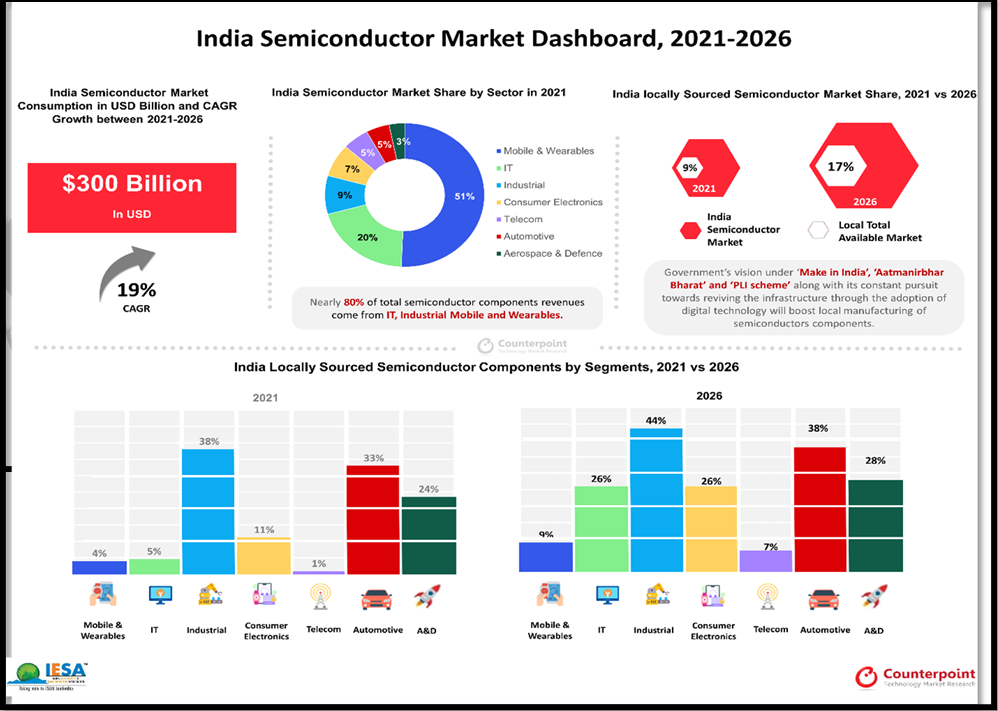
Source: Counterpoint
Highlight of the Editorial:
- Shift in the Era:
- Swadeshi Movement: The swadeshi movement promoted the use of handspun cloth and khadi as a means to foster self-sufficiency and economic independence from colonial rule.
- Modern Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s focus on semiconductor manufacturing represents a modern iteration of the swadeshi spirit, emphasizing technological self-reliance and innovation.
- Transition in Economic Paradigms: India’s shift from traditional handloom production to high-tech semiconductor manufacturing signifies a transition in economic paradigms, reflecting the country’s evolution in the global marketplace.
- Strategic Importance: The semiconductor industry holds strategic significance in driving innovation, economic growth, and national security, making India’s foray into this sector crucial for its future development.
Evolution of India’s Self-Reliance Journey:
- Khadi Movement: The birth of India’s swadeshi movement in 1918 with the establishment of the Sabarmati Ashram, promoting indigenous handloom and khadi production.The khadi movement, initiated by Gandhi ji , aimed to promote indigenous textile production and empower rural communities through cottage industries.
- All India Khadi Board: Formed in 1924, the board institutionalized khadi production, fostering self-reliant socio-economic development and rural empowerment.
- Promotion of Indigenous Goods: The All India Khadi Board played a pivotal role in promoting indigenous goods, fostering self-sufficiency, and reducing dependency on imported goods.
- Cultural Symbolism: Khadi became a symbol of Indian identity and resilience, representing the country’s quest for independence and economic self-reliance.
- Impact on Rural Economy: The khadi movement revitalized rural economies by creating employment opportunities and empowering local artisans and weavers.
- Continued Relevance: Despite technological advancements, khadi continues to hold cultural and economic significance, embodying the principles of sustainability and self-reliance.
Global Chip Manufacturing Landscape:
- Geopolitical Dynamics: The global chip manufacturing industry is shaped by geopolitical tensions, technological advancements, and economic interests, with major players vying for dominance.
- “Chip Wars” : Chris Miller’s “Chip Wars” outlines the geopolitical, technical, and economic forces shaping the global chip manufacturing industry.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The Covid-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in the chip supply chain, disrupting industries reliant on semiconductor components such as automotive and consumer electronics.
- Strategic Importance:
Semiconductor technology is vital for national security, defence, and economic competitiveness, driving nations to invest in research, development, and manufacturing capabilities.
- Emerging Trends: The rise of artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, and 5G technology has increased demand for semiconductors, amplifying competition among industry players.
- Government Interventions:
Governments implement policies and initiatives to bolster domestic semiconductor manufacturing, safeguarding national interests and fostering technological innovation.
Geopolitical Dynamics of Chip Technology:
- Government Interventions: Nations like the US and Taiwan implement policies to maintain technological supremacy, exemplified by the CHIPS Act and Taiwan’s engagement with TSMC.
- Technological Advancements: Shrinking chip sizes and scale economies drive government initiatives to bolster research and development in semiconductor manufacturing.
India’s Semiconductor Mission (ISM) :
- Introduction of ISM: The India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) aims to build a self-reliant semiconductor ecosystem in India, fostering indigenous chip manufacturing and promoting electronics manufacturing.
- Strategic Investments: ISM allocates ₹76,000 crore to support research, development, and infrastructure for semiconductor manufacturing, positioning India as a global hub for electronics production.
- Collaborative Efforts: ISM encourages collaboration between government, industry, and academia to drive innovation, skill development, and technology adoption in the semiconductor sector.
- Inclusive Growth: ISM focuses on inclusive growth by creating employment opportunities, fostering entrepreneurship, and bridging the digital divide through accessible and affordable technology solutions.
- Future Prospects: ISM holds promise for India’s economic growth, technological advancement, and global competitiveness, paving the way for transformative developments in the semiconductor industry.
| CASE STUDY : Success Stories
· Nvidia’s Market Surge: Nvidia’s market capitalization growth due to the AI wave positions it as a key player in the semiconductor industry, with significant implications for global tech dominance. · Japanese Chip Manufacturers: Japanese chip equipment manufacturers experience substantial market cap growth, reflecting the industry’s transformative shifts and advancements. |
India’s Role in Semiconductor Manufacturing:
- Research Capacity Building: Establishment of the Bharat Semiconductor Research Centre to enhance indigenous chip design and development capabilities.
- Strategic Partnerships: Tata Electronics’ investments in semiconductor manufacturing facilities, coupled with strategic partnerships with global players, signify India’s entry into the semiconductor race.
Opportunities & Way Forward:
- Workforce Development: The semiconductor industry presents opportunities for skilled professionals in research, design, manufacturing, and engineering, driving employment and economic growth.
- Strategic Positioning: India’s strategic location and growing capabilities in semiconductor manufacturing position it as a key player in the global supply chain, offering geopolitical advantages and investment opportunities.
- Technological Innovation: India’s focus on semiconductor manufacturing catalyzes innovation, research, and development in emerging technologies, fostering a culture of entrepreneurship and technological leadership.
- Infrastructure Development: Investments in infrastructure, research facilities, and human capital are essential to support India’s semiconductor ambitions and ensure long-term sustainability and competitiveness.
- Regulatory Framework: A supportive regulatory framework, intellectual property rights protection, and ease of doing business are crucial for attracting investments, fostering innovation, and ensuring a conducive environment for semiconductor manufacturing.
Conclusion:
From Gandhi’s charkha to Modi’s chip, India’s transition in the semiconductor era reflects its journey towards technological self-sufficiency and global competitiveness.
The launch of ISM and strategic investments in semiconductor manufacturing underscore India’s commitment to fostering innovation, economic growth, and self-reliance in the semiconductor industry.
As India embarks on this transformative journey, it stands poised to emerge as a key player in the global semiconductor landscape, shaping the future of technology and innovation.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the strategic importance of semiconductor manufacturing in driving innovation, economic growth, and national security. Evaluate the efficacy of India’s Semiconductor Mission (ISM) in fostering indigenous chip manufacturing and positioning India as a global hub for electronics production.