Trump’s Tariff Policy Sparks Global Economic Uncertainty
Why in the News?
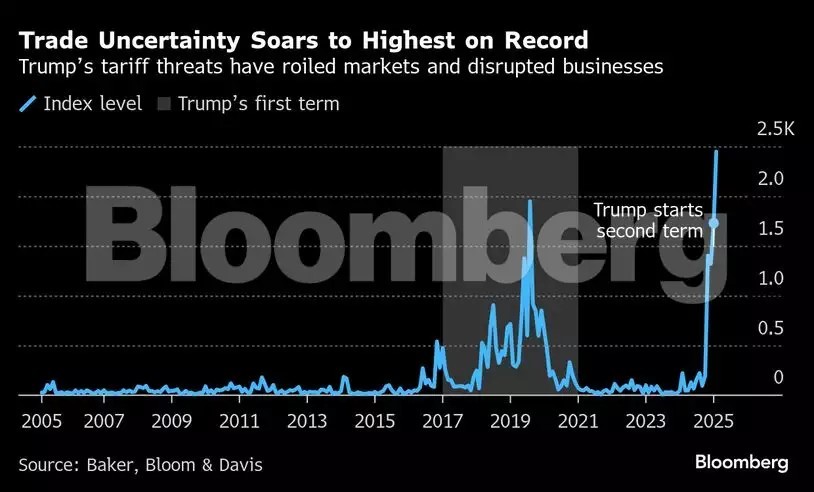
President Donald Trump announced reciprocal tariffs on major US trade partners, aiming to reduce the trade deficit and boost domestic manufacturing. However, retaliatory tariffs, market instability, and rising economic uncertainty have raised concerns about a potential global recession.
Key Announcements and Rationale:
- President Donald Trump announced “reciprocal tariffs” on US trade partners starting April 2 to counter what he calls an “unfair” trade system.
- Countries affected include the European Union (EU), China, Brazil, India, Mexico, and Canada.
- Trump believes tariffs will reduce the trade deficit, boost American manufacturing, and create jobs.
- He argues that US allies must contribute financially if they benefit from trade or US protection.
Emerging Fallout of Tariffs
- Many experts warn that tariffs are counterproductive and could push the US economy into recession.
- China and Canada have retaliated with counter-tariffs, and Mexico is preparing similar measures.
- The EU is strengthening its economy, with Germany planning major investments in defense and infrastructure.
- Trade policy uncertainty has surged, leaving businesses uncertain about future costs, demand, and hiring decisions.
Economic Indicators and Global Reactions
- Stock markets reflect concern: The S&P 500 has declined, while European indices like Stoxx 600, CAC 40, and DAX have performed better.
- US dollar weakens: The dollar has depreciated against the euro, Canadian dollar, Japanese yen, and Chinese yuan.
- Bond yields rise in Europe: Investors anticipate higher borrowing as countries issue new bonds to support domestic economies.
- The global response signals a potential shift in economic power and long-term consequences for US trade policies.
Reciprocal Tariffs: Key Points
- Definition: A trade policy where a country imposes tariffs equal to those levied by its trading partner to ensure fair trade.
- Purpose: Aims to balance trade relationships, retaliate against high tariffs, and serve as a negotiation tool.
- Historical Examples:
- Cobden-Chevalier Treaty (1860) – Promoted trade liberalization in Europe.
- Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act (1930) – Led to global retaliatory tariffs.
- U.S.-China Trade War (2018-2020) – Both nations imposed reciprocal tariffs.
- Impacts:
- Protects domestic industries but raises consumer prices.
- Strains international relations, leading to trade wars.
- Disrupts global supply chains, affecting market stability.