The start-up nation: key strategies for economic growth
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- India’s economic growth and management
- Start-up ecosystem in India
Why in the News?
India’s rapid economic growth is driven by digital innovation, a thriving startup ecosystem, and an evolving higher education system. To sustain and amplify this growth, India must integrate education, entrepreneurship, and employment, addressing global competitiveness and domestic needs.
Economic Growth Drivers
- Key Milestones: India’s economic expansion has been driven by the introduction of UPI, the telecom revolution providing affordable data, and a pandemic-driven surge in e-commerce and startups.
- GDP Progress: India’s nominal GDP is set to hit $3.9 trillion in 2024. Achieving this milestone took progressively shorter periods—60 years to reach $1 trillion, seven years for the second trillion, and five years for the third.
- Global Standing: India surpassed the UK in 2022 to become the fifth-largest economy. This rapid ascent reflects India’s growing influence in the global economic landscape.
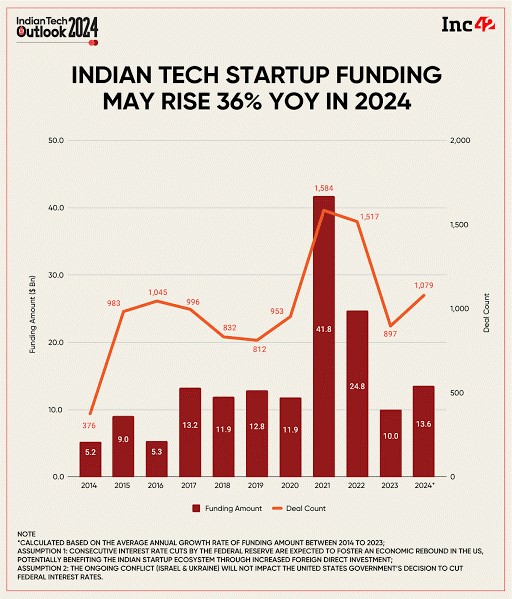
- Start-Up Ecosystem: With over 4 lakh startups, India ranks third globally in startup activity. The country adds new startups daily and sees a unicorn emerge every 20 days, indicating a vibrant entrepreneurial environment.
- Sectoral Influence: Advances in digital infrastructure have significantly contributed to the growth of the startup ecosystem, positioning India as a crucial player in the global economy.
Impact of Digital Infrastructure and Education
- Digital Access: Government capital expenditure and the telecom revolution have boosted internet access, with India offering some of the lowest data rates globally. Over 80 crore people use the internet, and 120 crore have cell phones.
- Higher Education Expansion: India’s higher education system includes 3 crore students across 1,168 universities and 45,473 colleges. The number of graduates entering the workforce annually is projected to rise from 1 crore in 2023 to 2.4 crore by 2050.
- Employment Trends: Industry 5.0 technologies like AI and robotics are likely to reduce demand for routine jobs while increasing the need for skilled professionals.
- Start-Up Opportunities: Digital expansion lowers customer acquisition costs for startups, enhancing opportunities in agriculture, e-learning, and financial inclusion.
- Future Outlook: Addressing the challenges posed by technological advancements and aligning education with job market needs are crucial for sustaining economic growth.
Innovation and Employment Potential
- Job Creation: DPIIT-recognized startups have created over 15.5 lakh direct jobs since 2017. In 2023, these startups generated 3.9 lakh jobs, marking a 46.6% annual increase and a 217.3% rise over five years.
- Global Comparison: US startups created nearly 37 lakh new jobs in 2022. Indian startups contributed $140 billion to the economy in FY23, about 4% of India’s GDP.
- UK Benchmark: In contrast, UK startups contributed £196 billion in FY23, accounting for6% of the UK’s GDP. This highlights significant growth potential for India’s startup sector.
- Entrepreneurial Trends: A global survey found that 11% of students from leading economies run businesses. In comparison, less than 2% of Indian HEI graduates pursue entrepreneurship.
- Potential Impact: If 5% of Indian graduates opted for entrepreneurship, it could result in 5 lakh new entrepreneurs annually. Despite a 90% failure rate, this would lead to 50,000 surviving startups, creating 5.5 lakh direct jobs and 55 lakh indirect and gig jobs each year.
Integrating Education, Entrepreneurship, and Employment
- Entrepreneurial Metrics: HEIs should expand their success metrics to include the creation of student-led ventures. This would emphasize entrepreneurship alongside traditional job placements.
- Academia-Industry Linkage: Strengthening the interface between academia and industry is essential. This includes supporting, mentoring, and funding research ideas to translate into successful ventures.
- Global Best Practices: The US experience shows that academic tech transfer has significantly contributed to industry output and job creation. Over 20 years, this process added $1 trillion to industry output and created over 40 lakh jobs.
- R&D Investment: To compete globally, India must increase R&D investment, currently at 0.7% of GDP, with only 10% of this allocated to HEI research. Higher R&D spending is crucial for fostering innovation.
- Strategic Focus: Higher education should be viewed strategically for economic development. Integrating education with entrepreneurship and building a robust academia-industry interface will drive economic growth and job creation.
Way Forward / Recommendations for India:
- Systematic Approach: India needs a systematic strategy to integrate education, entrepreneurship, and employment. Aligning educational outcomes with industry needs and fostering a supportive environment for startups is crucial.
- Policy Support: Government policies should encourage entrepreneurship and innovation, providing necessary support for startups and enhancing the academia-industry linkage.
- Education Reform: The education system should focus on developing entrepreneurial skills and fostering innovation. Curricula should be revised to include entrepreneurship training and resources for startup ventures.
- Increased R&D Investment: Boosting investment in R&D, especially in higher education institutions, is essential for maintaining global competitiveness and driving economic growth.
- Economic Vision: To achieve rapid economic growth during the Amrit Kaal, India must integrate education, entrepreneurship, and employment into a cohesive strategy. This approach will support sustainable development and enhance India’s global economic position.
Conclusion
India’s economic trajectory is promising, with significant contributions from digital infrastructure and startups. However, to achieve sustained growth, it must strategically integrate education, entrepreneurship, and employment, enhancing its global standing and fostering a robust economic environment.
Source: Indian Express
Mains Practice Question
Discuss the role of digital infrastructure and higher education in driving India’s economic growth. How can India integrate education, entrepreneurship, and employment to sustain and amplify this growth? Analyze the potential challenges and suggest policy measures to address them.