THE ROLE OF X CHROMOSOME IN AUTO-IMMUNE DISEASES
Focus:
- Recent focus on X chromosome’s role in autoimmune diseases.
- Research suggests XIST molecule involvement.
About Auto- Immune Disease:
- When the body’s natural defence mechanism can’t distinguish between your cells and alien cells, it develops a condition called autoimmune disease and unintentionally attacks healthy cells.
- Study Findings :A 2023 University of Oxford study found that 10% of the population studied had autoimmune diseases, with 13% women and 7% men affected.
- Role of X Chromosome: Women, having two X chromosomes, exhibit a molecular coating crucial for X-chromosome inactivation, ensuring gene regulation.
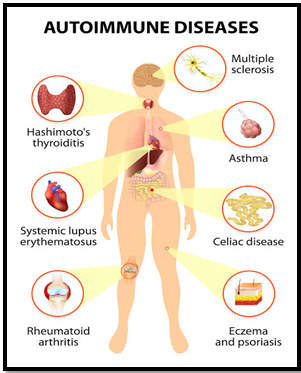
Common Auto-immune diseases
- Psoriasis: The causes skin cells to multiply too quickly
- Rheumatoid arthritis: The immune system attacks the joints.
- Addison’s disease: It affects the adrenal glands, which produce the hormones cortisol and aldosterone
- Graves’ disease: It attacks the thyroid gland in the neck.
| What is Molecule?
· XIST is an RNA molecule crucial for X-chromosome inactivation, a process where one of the two X chromosomes in female mammals becomes transcriptionally silent. · It plays a key role in choosing which X chromosome remains active and in initiating gene silencing on the inactive X chromosome. |