THE FADING ROLE OF UNIVERSITIES IN INDIA
Syllabus:
- GS 2 : Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education
Why in the News ?
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) directive mandates universities to display government logos, raising concerns about academic freedom.
- This reflects a broader trend of the government’s intrusion into educational institutions, undermining the role of universities as spaces for free thought.
Source : Down to Earth
Instances of Assault on Academic Freedom:
- UGC’s history of government directives includes promoting political agendas, like displaying the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao logo.
- Previous mandates involved universities in activities like G-20 awareness and Swachhatha campaigns.
- The directive to create selfie points with the Prime Minister showcases a growing trend of politicizing academic spaces.
- Current government, ironically led by those opposing the 1970s Emergency, seems to follow similar tactics to suppress dissent.
- Recent instances like IISc cancelling discussions on UAPA and fines imposed at JNU reveal attempts to stifle academic freedom.
- Resignations of scholars at Ashoka University due to political pressure underscore the prevailing climate of suppression.
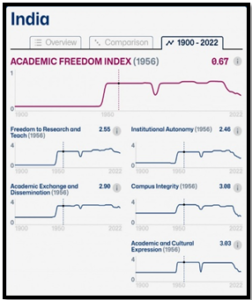
| About Academic Freedom Index Report 2022
· Published by the Global Public Policy Institute, this index is a global time-series dataset (1900-2019). · Developed with Friedrich-Alexander University, Scholars at Risk, and the V‑Dem Institute. · Assesses academic freedom in 179 countries through indicators like research freedom, academic exchange, and institutional autonomy. Key Indicators: · Freedom to Research and Teach · Freedom of Academic Exchange and Dissemination · Institutional Autonomy of Universities · Campus Integrity · Freedom of Academic and Cultural Expression Global Overview: · Identifies 22 countries, including India, China, the United States, and Mexico, experiencing reduced academic freedom. · Only five small countries improved, while 152 nations stagnated, reverting to academic freedom levels of four decades ago. |
Declining Academic Freedom:
- India’s academic freedom index, as per the V-Dem Institute, places it in the bottom 30% globally.
- The score of 0.38 is lower than even Pakistan (0.43), reflecting a worrying decline compared to the Emergency years.
- India’s Performance Metrics:
- Campus Integrity: India records low scores.
- Institutional Autonomy: India’s performance is subpar.
- Academic and Cultural Expression: India fares poorly.
- Research and Teach, Academic Exchange: India performs slightly better.
- Such low rankings signal an alarming trend that threatens the core principles of democratic discourse.
Factors Contributing to India’s Decline:
- Significant decline since 2013, intensified post-2014 election.
- Lack of legal safeguards for academic freedom, enabling attacks.
- Pressure on institutional dimensions and constraints on academic freedom due to the ruling government’s policies.
Role of Universities in Democracy:
- Free Thought: They uphold the freedom of thought, encouraging diverse perspectives and fostering an environment for dissent and dialogue.
- Intellectual Hubs: Universities serve as intellectual hubs fostering critical thinking, innovation, and knowledge dissemination.
- Research and Awareness: Universities contribute to informed decision-making by conducting research, providing data, and raising societal awareness.
- Civic Engagement: Through education, they prepare individuals for active civic engagement, promoting democratic values and responsible citizenship.
- Social Equality: Universities play a role in addressing social inequalities by providing education as a means of empowerment.
- Policy Influence: Academic research and expertise influence policies, ensuring evidence-based governance.
- Global Citizenship: They cultivate a sense of global citizenship, promoting cross-cultural understanding and cooperation.
- Institutional Autonomy: Maintaining institutional autonomy safeguards universities as independent entities critical for a thriving democracy.
Challenges (to Institutional Autonomy):
- Unlike countries like New Zealand, India lacks explicit mention of academic freedom in its constitution.
- Freedom of speech, a constitutional guarantee, faces challenges through sedition laws, Section 295A, and defamation suits.
- Misuse of these legal provisions has become a tool to silence artists and scholars, limiting academic autonomy.
- The UGC’s increasing interference in university appointments and the erosion of institutional autonomy are detrimental.
- Politically motivated appointments compromise merit-based selections, impacting the overall quality of academic leadership.
Note: This contradicts the UGC Act of 1956, which emphasizes monitoring standards in consultation with universities.
Way Forward : Protecting Academic Freedom
- Legal Protection: Establish robust legal safeguards ensuring academic freedom, shielding scholars from interference.
- Institutional Independence: Safeguard university autonomy, minimizing political influence in leadership selection and decision-making.
- Global Collaboration: Foster international partnerships to bolster academic freedom globally.
- Public Awareness: Educate the public on academic freedom’s role in societal progress and democratic values.
- Faculty Contracts: Include explicit clauses protecting scholars’ academic freedom in employment contracts.
- Educational Modules: Integrate academic freedom education into curricula to emphasize diverse perspectives.
- Neutral Research Funding: Maintain impartial research funding to support unbiased investigations.
- Policy Advocacy: Advocate for policies that reinforce academic freedom, addressing legal gaps and preserving this fundamental principle.
As India commemorates its 75th year as a Republic, there’s a pressing need to reflect on the vision of Tagore for a nation “where the mind is without fear.”
Political parties should engage with faculty bodies and student associations to address the current state of academic freedom, ensuring universities remain bastions of free thought and expression.
Mains Practice Questions:
Critically analyze the declining state of academic freedom in India, focusing on the recent UGC directive and ways to protect academic freedom.

 Source : Down to Earth
Source : Down to Earth

