THE EXAMINATION SYSTEM EVALUATION
Syllabus:
- GS 2: Education ,Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, and Education.
Why in the News?
- Media reports highlight scandals that mar universities and school boards during examination seasons.
Focus : Credibility of Examinations
- Credibility ties directly to the standard of certificates issued.
- Lack of credibility affects educational standards, shaping learning based on examination patterns, often favouring memorization.
Source: Researchgate
Constitutional Provisions on Education:
- Fundamental Right :
- Article 21 (A) : Right To Compulsory Education.
- Directive Principles of State Policy:
- Article 41: Ensures the right to work, education, and public assistance in certain cases.
- Article 45: Provides for free and compulsory education for children.
- Article 46: Ensures early childhood care and education to children below the age of six years.
- Fundamental Duties:
- Article 51A: Mandates parents or guardians to provide opportunities for education to their children or wards between the ages of six and fourteen years.
| Overview:
Evolution of Modern Education System in India 1. East India Company Era (1600s-1858): · Vernacular schools focused on local languages. · Education mainly for the elite, emphasizing traditional knowledge. 2. British Period (1858-1947): · Wood’s Despatch (1854): Laid the foundation for a systematic education system. · Indian Education Act (1901): Shifted control to provinces. 3. Post-Independence (1947 onward): · Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (2000): Aimed at universal elementary education. · Right to Education Act (2009): Ensured free and compulsory education for children aged 6-14. 4. Current Era: · National Education Policy (2020): Focused on holistic learning, skill development, and flexibility. · Emphasis on digital learning, vocational training, and a more inclusive approach |
Challenges in the Education System:
Lack of Resource:
- As per the Economic Survey 2022-23, the proportion of total expenditure allocated to education in the budget has decreased from 10.4% to 9.5% over the last seven years.
Inconsistencies in Examination Systems:
- Summative examinations lack consistency over time and comparability across institutions.
- Concerns arise about examinations primarily testing memory, promoting rote learning, and failing to assess higher-order thinking skills.
Flaws in Examination Papers and Evaluation:
- Instances of flawed question papers with language errors, conceptual mistakes, and irrelevant questions.
- Indiscriminate evaluation of answer scripts, leading to grades that don’t reflect true learning achievements.
Decentralized System Challenges:
- India has over 1,100 universities, 50,000 affiliated colleges, and 60 school boards.
- Secrecy and standardization are seen as essential, but unchecked secrecy can lead to scandals, and excessive standardization hampers innovation.
Employability Concerns:
- Employers often rely on their assessments rather than institutional certifications.
- Rise of a coaching market for competitive examinations and skill development due to institutional shortcomings.
Assessment Quality and Oversight:
- Emphasis on outcome-based learning in regulations, but inadequate oversight allows deviations.
- Lack of alignment between syllabi, teaching, and imparting higher-order thinking skills.
Secrecy and Standardization Challenges:
- The secrecy involved in the examination process facilitates the
- The move towards academic autonomy lacks oversight, and standardization is compromised.
Source: India Briefing
| Government Initiatives :
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA): o A flagship program for universalizing elementary education across India. o Aims at providing quality education to all children aged 6-14 years. Mid-Day Meal Scheme: Provides free, nutritious meals to school children to improve attendance and nutrition levels. Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA):Focuses on improving secondary education with a goal to increase enrollment and retention. National Means-Cum-Merit Scholarship Scheme (NMMSS):Provides scholarships to economically weaker students to encourage them to continue education. National Scholarship Portal (NSP): An online portal for various scholarships to students at different levels. Pradhan Mantri Vidya Lakshmi Karyakram: Aims to provide financial support for students pursuing higher education through education loans and scholarships. Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan: Integrates various school education schemes to ensure holistic development of students. National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS):Encourages industries to engage apprentices and provides apprenticeship training. Udaan Scheme: Aims at addressing the low enrollment of girl students in prestigious engineering institutions. |
Source: ToI
Way Forward:
- Specify Minimum Learning Standards:
- Define minimum learning outcomes to guide educational institutions.
- Encourage various approaches to achieve these standards.
- Continuous Assessment and Transparency:
- Implement continuous assessment with teacher involvement.
- Introduce transparency in summative assessments with checks and balances.
- Leverage Technology:
- Standardize question paper setting and evaluation using technology.
- Utilize software solutions for centralized and distributed assessments.
- Codify Negligence and Fraud:
- Establish codes addressing negligence, fraud, and academic inadequacies.
- Link corrective measures and punishments to these codes.
- External Audit:
- Conduct external audits of assessment systems in universities and school boards.
- Evaluate processes based on established principles and benchmarks to ensure reliability and consistency.
- Secrecy and standardization:
- Secrecy and standardization, essential in good examination boards, need careful balancing to prevent scandals and hinder experimentation.
- Transparency and Credibility:
- Release audit reports regularly, ensuring transparency in the examination process.
- Grade examination boards on transparency, reliability, and consistency.
Striking a balance between secrecy and transparency is crucial for a credible examination system.
The focus should be on ensuring minimum standards, continuous assessment, leveraging technology, and conducting external audits to enhance transparency and credibility in the education system.
Mains Practice Question:
Despite constitutional mandates and numerous government initiatives, India’s education system struggles with unreliable examinations plagued by scandals. Critically analyze the key challenges in ensuring the credibility of examination

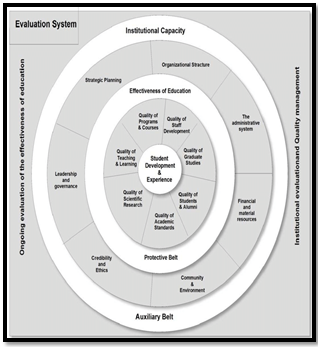 Source: Researchgate
Source: Researchgate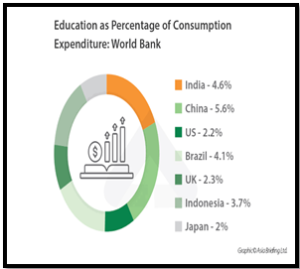 Source: India Briefing
Source: India Briefing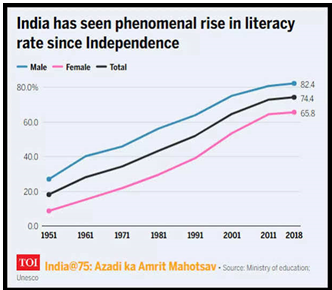 Source: ToI
Source: ToI

