THE EUROPEAN UNION’S ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ACT
Objectives of the EU AI Act:
Regulatory Framework:
- Develop the world’s first legislation on AI for creating regulatory standards.
- Mitigate risks associated with AI systems.
Guidelines for Stakeholders:
- Establish clear guidelines for developers, users, and regulators in the AI sector.
Source: UGI
Features of the Act:
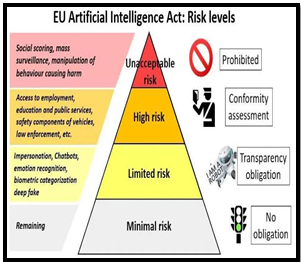
Risk-Based Approach:
- Categorize AI applications into risk levels, allowing tailored regulations.
- Higher-risk applications subjected to more stringent requirements.
Prohibitions:
- Explicitly prohibit certain AI practices like social credit scoring systems and predictive policing applications.
Emphasis on Transparency:
- Mandate developers to provide clear information on AI system capabilities and limitations.
- Ensure users can make informed decisions.
Conformity Assessment:
- Introduce independent conformity assessment for higher-risk AI applications.
- Enhance objectivity and reduce conflicts of interest in regulatory processes.
Reporting and Enforcement:
- Individuals can report non-compliance.
- Member states’ market surveillance authorities responsible for enforcing the AI Act.
Fines and Penalties:
- Specific limits on fines for SMEs and start-ups.
- Fines range from $8 million to almost $38 million, depending on the nature of the violation and company size.
Limitations:
Challenges in Definition:
- Criticisms about accurately defining and categorizing AI applications.
- Evolving AI technologies may lead to uncertainties in regulatory implementation.
Competitiveness Concerns:
- Stringent regulations might hinder European businesses’ competitiveness globally.
- Potential impact on innovation and AI development outside the EU.
Burden on Smaller Businesses:
- Compliance with the EU AI Act may disproportionately affect smaller businesses and start-ups.
- Resources required for conformity assessments may limit their ability to compete.
Potential Implications:
Global Impact:
- Influence AI development beyond EU borders, setting a global precedent.
- Similar to the MiCa regulation’s impact on crypto-assets globally.
Ethical Considerations:
- Contribute to global norms for AI development by prioritizing ethics and fundamental rights.
- Balance between regulation and fostering innovation is crucial.
International Collaboration:
- Encourage collaboration and cooperation between regulatory authorities.
- Foster a unified approach to AI regulation globally.
The EU AI Act represents a significant step in regulating AI technologies responsibly, addressing concerns while acknowledging potential challenges and drawbacks.

 Source: UGI
Source: UGI

