The Baltic Sea: A Vital Yet Vulnerable Waterway
Why in the news?
The Baltic Sea’s strategic importance is growing amidst geopolitical tensions, including suspected sabotage of undersea cables. Swedish officials highlight its security risks, emphasizing its vital role in European commerce and security, making it a high-risk zone.
Overview of the Baltic Sea:
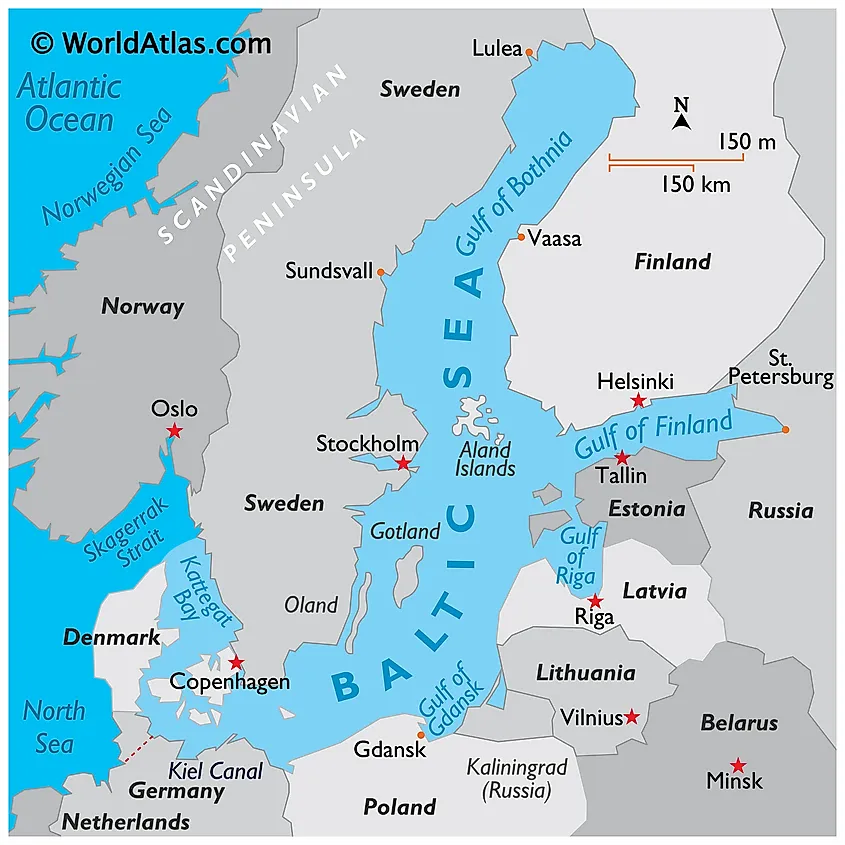
- Geography: The Baltic Sea is a semi-enclosed inland sea in Northern Europe, spanning 377,000 sq. km.
- Dimensions: It stretches 1,600 km in length and 193 km in width, with an 8,000 km coastline shared by nine countries: Denmark, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Russia, Finland, and Sweden.
- Salinity: Known as the world’s largest brackish water body, its low salinity results from the inflow of over 250 rivers, including the Neva River.
Strategic and Economic Importance:
- Connection to Oceans: The Baltic Sea connects to the North Atlantic Ocean through the Danish Straits and to the White Sea via the White Sea Canal.
- Gulfs and Islands: Key gulfs include the Gulf of Bothnia, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Riga. The sea also hosts over 20 islands, with Gotland (Sweden) being the largest.
- Economic Significance: The Baltic Sea is crucial for European commerce and security, with vital shipping routes and ports along its coast.
Geopolitical Tensions and Security Risks:
- Rising Tensions: The Baltic Sea is increasingly vulnerable due to geopolitical issues. This is evident from recent suspected sabotage of undersea cables.
- Swedish Concerns: Sweden’s Prime Minister has described the Baltic as a “high-risk” zone, highlighting the growing security threats in this vital waterway.
- European Security: The Baltic’s importance in regional stability makes it a focal point in European security discussions.
What is a Gulf?
- Definition: A gulf is a large portion of the sea almost surrounded by land, with a narrow opening.
- Formation: Gulfs are formed when rock collapses, land sinks, or through erosion.
- Process: These events create a large indentation, which is later filled with water.
Key Facts about the Baltic Sea:
- Location: Semi-enclosed inland sea in Northern Europe, an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean.
- Dimensions: 377,000 sq.km area, 1,600 km long, 193 km wide.
- Coastline: 8,000 km shared by 9 countries.
- Geographical Features: Connected to Atlantic via Danish Straits; contains Gulf of Bothnia, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Riga.
- Water Characteristics: Brackish water, lower salinity due to freshwater inflow.
- Rivers: Over 250 rivers, with Never being the largest.
- Islands: Home to 20+ islands, Gotland being the largest.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times