THE ADVENT OF A HOLISTIC APPROACH TO ‘ONE HEALTH’
Syllabus:
- GS 2: Health, Government Policies & Interventions, Issues Arising out of their Design & Implementation.
Focus:
- Under One health mission, a national network of high-risk pathogen (Biosafety level or BSL 3 and BSL 4) laboratories has been created
Source: X.com
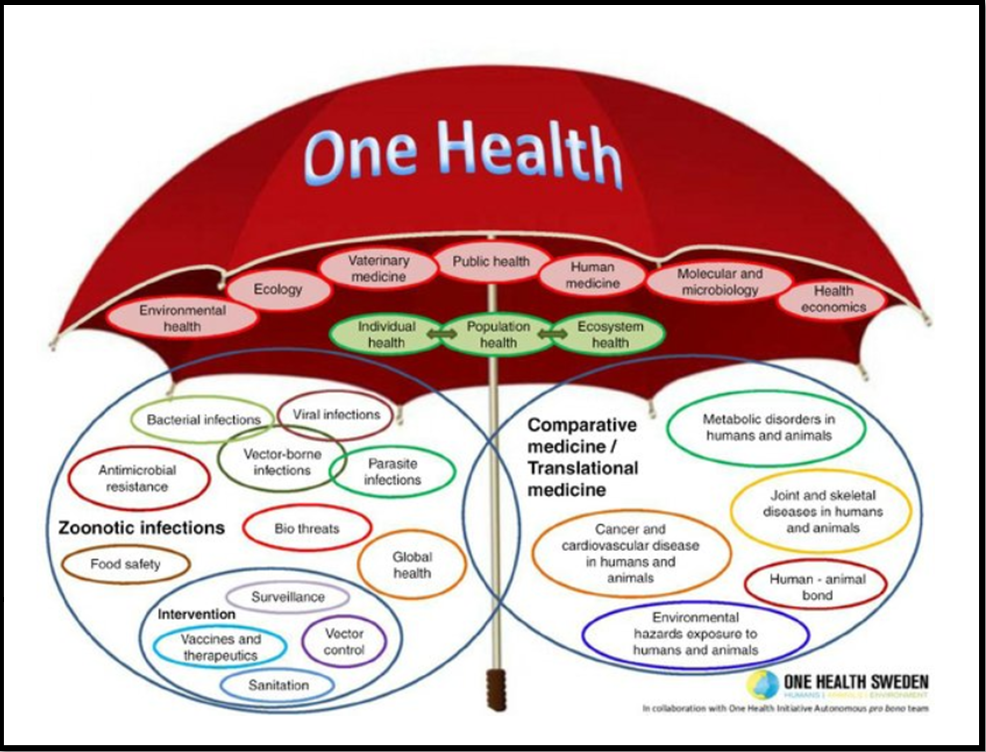
The advent of the ‘One Health’ approach marks a pivotal shift in how we perceive and manage health crises, emphasizing the intricate connection between human, animal, and environmental health. This holistic perspective is increasingly vital in the wake of global pandemics such as COVID-19, which illustrate the complex interplay between different species and ecosystems. The establishment of the National One Health Mission underscores a global movement towards unified health strategies that promise a more resilient future against health threats.
Interdependence and Impact of Pandemics
- The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the interconnectedness of humans, animals, and the environment.
- Livestock diseases, such as lumpy skin disease, demonstrate that pandemics affect more than just humans.
- The emergence of diseases in animals can significantly impact human health and global economies.
- A holistic approach, recognizing this interdependence, is essential for effective disease management and prevention.
- The spread of diseases from wildlife to livestock and humans highlights the need for integrated health strategies.
National One Health Mission: A Milestone
- Initiated by the Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC) in July 2022.
- Collaboration among 13 Ministries and Departments, including Health, Animal Husbandry, Environment, and Defence.
- The mission aims for holistic pandemic preparedness, integrating human, animal, and environmental health.
- The establishment of a National Institute for One Health in Nagpur as the coordinating body for national and international efforts.
- Laid foundation stone by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on December 11, 2022, marking a significant step towards integrated health management.
Goals and Approaches
- Development of integrated disease surveillance and joint outbreak response strategies.
- Promotion of coordinated research and development (R&D) across sectors to combat routine and pandemic diseases.
- Emphasis on seamless information sharing for efficient disease control and preparedness.
- The mission fosters a coordinated approach to manage diseases affecting humans, animals, and wildlife, aiming for better outbreak response.
- Focus on R&D to develop vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostics, involving government, academic centers, and the private sector.
Infrastructure and International Collaboration
- Creation of a national network of high-risk pathogen laboratories (BSL 3 and BSL 4) for improved disease outbreak response.
- Utilization of AI, machine learning, and disease modelling to enhance epidemiology and data analytic capabilities.
- Efforts to mainstream genomic surveillance and expand it to include livestock and wildlife for comprehensive disease monitoring.
- India’s G-20 presidency highlighted the global significance of ‘One Health’, encouraging international collaboration for better surveillance and response.
- The ‘One Health’ approach addresses broader concerns such as antimicrobial resistance, food safety, and climate change impacts, advocating for ‘One Earth, One Health’ and ‘Health for All’.
Why has the One Health Concept become more Important?
Source:- UGI
- Human Expansion: Human populations are growing and expanding into new geographic areas due to which close contact with animals and their environments provides more opportunities for diseases to pass between animals and people. Of the contagious diseases affecting humans, more than 65% are of zoonotic or animal to man origin.
- Environmental Disruptions: Disruptions in environmental conditions and habitats can provide new opportunities for diseases to pass to animals.
- International Travel & Trade: The movement of people, animals, and animal products has increased from international travel and trade due to which diseases can spread quickly across borders and around the globe.
- Viruses in Wildlife: Scientists have observed that there are more than 1.7 million viruses circulating in wildlife, and many of them are likely to be zoonotic. This implies that unless there is timely detection, India risks facing many more pandemics in times to come.
In conclusion, the ‘One Health’ initiative represents an evolutionary step in global health governance, bridging the gaps between disparate health domains to forge a comprehensive defense against future pandemics. By fostering collaboration across sectors and nations, it aims not only to mitigate immediate health crises but also to safeguard the wellbeing of future generations. The mission’s forward-looking stance on health underscores the imperative of unity in the face of shared vulnerabilities, heralding a new era of health diplomacy and intersectoral cooperation.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
- Discuss the significance of the ‘National One Health Mission’ in integrating human, animal, and environmental health strategies for pandemic preparedness in India. Illustrate with examples how this integrated approach can enhance disease surveillance and outbreak response.
- Evaluate the role of technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence and genomic surveillance, in the success of the ‘National One Health Mission’. How can these technologies improve India’s capacity to predict, prevent, and respond to emerging infectious diseases?
Associated Articles:
https://universalinstitutions.com/how-can-one-health-help-india-and-india-help-one-health/