LEGISLATIVE DECLINE IN INDIA: A DEEPENING CONCERN
Syllabus:
- GS2 : Parliament and State Legislatures—Structure, Functioning, Conduct of Business, Powers & Privileges and Issues Arising out of these.
Why in the News ?
- Recent events in the Indian Parliament, including a security breach and the subsequent government response, raise serious concerns.
- Individuals staged a theatrical attempt in Parliament, bringing attention to the issue of unemployment.
Source: ToI
Focus:
- The denial of a legislative debate on a crucial issue and the suspension of numerous Opposition members reflect disregard for deliberative democracy.
- The Union government’s response to this incident has been problematic and raises questions about democratic values.
Issues Citing Threat to Democratic Values and Legislative Decline:
Suspension of Opposition Legislators:
- The government’s refusal to engage in a debate and the subsequent suspension of 78 Opposition MPs highlight a worrying trend.
- The Chair’s unprecedented use of suspensions as a response to demands for statements and debates adds to the concern.
Selective Use of Suspension:
- Since 2014, 92 suspensions, primarily targeting Opposition members, have occurred, contrasting with a more inclusive approach from 2004 to 2014.
- Even less severe offenses have resulted in suspensions, raising questions about.
- the fairness and equity of such actions.
Erosion of Deliberative Democracy:
- Deliberation is a fundamental aspect of a functioning democracy, involving debates, committee discussions, and thorough examination of Bills.
- Recent parliamentary sessions have witnessed attempts to bypass the Opposition, pass Bills without sufficient discussion, and limit amendments.
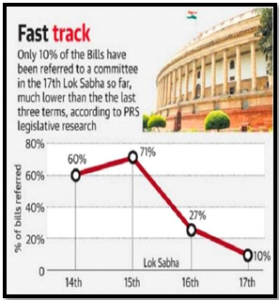
Underutilization of Committees:
- The underutilization of parliamentary and standing committees undermines the spirit of deliberation.
- Adequate discussions and in-depth considerations of Bills and legislations are essential for a healthy democracy.
Short Shrift to Legislative Business:
- Legislative business and parliamentary work have taken a backseat, with theatrics and one-upmanship dominating proceedings.
- Both the Treasury and Opposition benches have engaged in actions that compromise the essence of parliamentary democracy.
Misuse of Laws Against Dissent:
- The use of the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act to target dissenters reflects a concerning pattern.
- Equating dissent with terrorism contributes to a climate where genuine concerns are suppressed using draconian measures.
Global Democracy Reports:
- Global democracy reports, such as those by the V-Dem Institute, characterize India’s democracy as an “electoral autocracy.”
- India’s democratic credentials are further questioned as legislative actions prioritize theatrics over substantive debates.
Challenges in Legislative Reform in India:
- Political Resistance: Political parties may resist changes that could alter the balance of power or reduce their influence.
- Lack of Consensus: Difficulty in achieving consensus among diverse political ideologies and regional interests hinders the legislative reform process.
- Complex Procedures: Cumbersome legislative procedures and bureaucratic red tape impede the swift enactment of reforms.
- Absence of Legislative Impact Assessment Culture: The absence of a culture for comprehensive Legislative Impact Assessment makes it challenging to evaluate the true implications of proposed legislation.
- Resistance to Committee Reforms: Resistance to changes in parliamentary committees, such as longer tenures and increased specialization, may hinder their effective functioning.
- Political Whip Usage: Overreliance on the use of the whip in parliamentary proceedings limits free debate and deliberation.
- Speaker’s Role in Anti-Defection Law: Resistance to transferring the adjudicating power of the speaker regarding the anti-defection law to independent bodies like the Election Commission.
- Lack of Statutory Backing for Election Commission: The lack of a statutory framework supporting the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) poses challenges to the Election Commission of India’s enforcement capabilities.
- Opposition Empowerment: Establishing the institution of a Shadow Cabinet faces potential resistance, affecting the overall empowerment of the opposition.
- Historical Inertia: Prevailing norms and historical practices create inertia, making it challenging to break away from traditional legislative processes.
- Lack of Public Awareness: Limited public awareness about legislative reforms and their potential impact poses a challenge to garnering widespread support.
- Overloaded Legislative Agenda: A crowded legislative agenda often results in inadequate time for thorough deliberations on proposed reforms.
- Privilege Ambiguity: The ambiguity surrounding legislative privileges makes it difficult to codify and delineate the extent of immunity enjoyed by lawmakers.
- Federal Structure Complexities: The federal structure of India adds complexity, requiring coordination among states and the central government for effective legislative reforms.
International Concerns:
- International organizations, including Freedom House, have raised alarms about the state of civil and political liberties in India.
- The recent actions of the government contribute to a perception of India as “partially free,” inviting international scrutiny.
Way Forward for Legislative Reforms:
- Legislative Impact Assessment:
- Establish a comprehensive framework for both pre and post Legislative Impact Assessment.
- Mandate every legislative proposal to include a detailed analysis of social, economic, environmental, and administrative impacts for broader awareness and legal assessment.
- Form a new Legislation Committee in Parliament to oversee and coordinate legislative planning.
- Codification of Privileges:
- Define and limit the privileges of legislators to ensure the free and independent functioning of Parliament and state legislatures.
- Consider amending Article 105 to provide clarity on the extent of immunity enjoyed by members under parliamentary privileges.
- Parliamentary Committee Reforms:
- Implement measures for the effective functioning of Department Related Standing Committees, including longer tenures and promoting specialization.
- Review of Anti-Defection Law:
- Restrict the use of the whip to a no-confidence motion to revive debate and deliberations in Parliament.
- Transfer the adjudicating power of the speaker concerning the anti-defection law to the Election Commission of India.
- Strengthening of ECI :
- Provide statutory backing to the Model Code of Conduct, eliminating any vacuum for the Election Commission of India (ECI) to enforce it.
- Strengthen the Role of Opposition:
- Form the institution of a ‘Shadow Cabinet’ in India to bolster the role of the opposition.
- Adopting the British cabinet system, the shadow cabinet aims to balance the ruling cabinet and prepare opposition members for future ministerial roles.
- Introduce a system where each action of a Cabinet Minister must be countersigned by the corresponding minister in the shadow cabinet.
The recent developments in India’s Parliament underscore a worrying decline in democratic values.
From the suppression of debates to the selective suspension of Opposition members, these actions contribute to a broader backsliding of democracy in the country, demanding urgent attention.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
Examine the challenges contributing to the legislative decline in India. Propose comprehensive reforms and suggest the way forward for strengthening deliberative democracy in the country.

 Source: ToI
Source: ToI

