TB CONTROL IN INDIA CALLS FOR PERSON-CENTRED SOLUTIONS
Syllabus:
General Studies-II: Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Why in the news?
The call for person-centred solutions in TB control in India highlights the urgent need for improved healthcare strategies.
- Tuberculosis (TB) remains a global and national public health challenge.
- India aims to eliminate TB, but progress is slow, and access to quality care remains limited.
source:pib
About the Urgent Need for Paradigm Shift:
- The paradigm shift is necessary to prioritise the needs and interests of TB patients and communities.
- Person-centred care and management are crucial for effective TB control.
- Communities and survivors advocate for change, influencing government approaches.
- Initiatives like nutritional support and addressing stigma and gender aspects are essential but need further development.
| What is Tuberculosis?
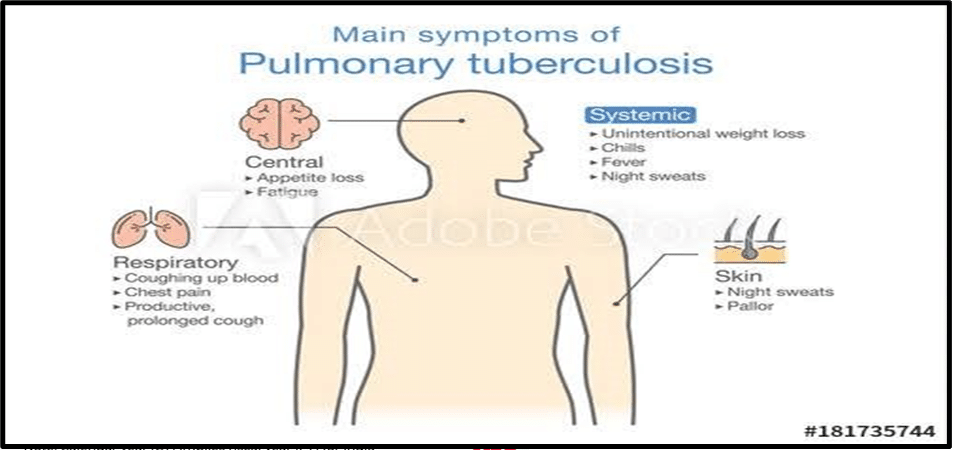
● TB is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs. ● It spreads through the air when infected individuals cough, sneeze, or spit. ● Symptoms: include coughing with sputum and blood, chest pains, weakness, weight loss, fever, and night sweats. ● Vaccine: Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is a vaccine available for TB. Understanding Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan: ● Initiative of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MOHFW) aimed at accelerating India’s progress towards TB elimination by 2025. Objectives: ● Provide additional patient support to improve treatment outcomes. ● Increase community involvement to meet the goal of ending TB by 2025. ● Utilise Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) activities for TB eradication efforts. Components: Ni-kshay Mitra Initiative: ● Provides additional diagnostic, nutritional, and vocational support to TB patients. ● Ni-kshay Mitra (Donor) individuals or organisations support health facilities, blocks/urban wards/districts/states to enhance TB response. Ni-kshay Digital Portal: ● Online platform facilitating community support for individuals with TB. ● Enables coordination and collaboration among stakeholders involved in TB eradication efforts. Understanding the Diagnostic Methods: ● Screening for symptoms, X-ray imaging, sputum microscopy, molecular tests, and alternative sample collection methods are used for TB diagnosis. ● PCR machines and the urine LAM test can aid in more efficient TB detection. |
Global Statistics:
- In 2020, 1.5 million TB-related deaths and 10 million new TB cases worldwide.
- India has the highest TB burden globally, with 26 lakh new cases and approximately 4 lakh deaths annually.
- India faces significant challenges in TB control due to poor rural healthcare infrastructure, unregulated private healthcare leading to drug misuse, poverty, lack of political will, and administrative corruption.
About the initiatives regarding Tuberculosis:
Global Initiatives:
- “Find. Treat. All. #EndTB” Initiative: Launched by the WHO, in collaboration with the Global Fund and Stop TB Partnership, aimed at accelerating efforts to end TB globally.
- Global Tuberculosis Report: Released annually by the WHO, providing comprehensive information on the global TB situation and progress towards TB elimination.
India’s Initiatives:
- National TB Elimination Programme: Strengthened to achieve the goal of ending the TB epidemic in India by 2025, five years ahead of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) target for
- National Strategic Plan (NSP) for Tuberculosis Elimination (2017-2025): Outlines strategies and actions to eliminate TB in India.
- Nikshay Ecosystem: National TB information system facilitating TB case management, monitoring, and reporting.
- Nikshay Poshan Yojana (NPY): Provides financial support of Rs 500 to TB patients through direct benefit transfer.
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign: National campaign aimed at raising awareness about TB prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Vaccine Development:
- VPM 1002 and MIP: Two vaccines identified for TB, currently undergoing Phase-3 clinical trials.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Mission:
- Government initiative focused on utilising technology and digital health IDs for TB patients under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Mission to ensure efficient diagnostics and treatment.
Challenges:
TB Challenges in India:
- Despite goals for elimination, TB remains a significant health challenge in India, with slow progress.
- Shift towards patient-centred care is crucial, focusing on the needs of TB-affected individuals.
- Understanding patients’ experiences is vital for effective care.
Advocacy and Policy Changes:
- Advocacy by TB survivors has influenced policy changes and improved support, but gaps in care persist.
- Improvements needed in diagnosis, treatment access, especially in rural areas, and ensuring quality drugs.
Humane Care Approach:
- Mental health support and gender-responsive care are essential for a more humane TB care approach.
- Socio-economic factors like poverty and nutrition must be addressed to combat TB effectively.
World TB Day and Persistent Challenges:
- Despite advancements since 1962, TB remains a global health issue, with India facing a significant burden.
- The 2024 theme emphasises the urgency and possibility of overcoming TB.
Types of TB and Challenges:
- Various forms of TB exist, including drug-resistant TB, posing challenges in management and treatment.
- The 10-point agenda focuses on early detection, treatment adherence, and addressing drug resistance.
Diagnostic Challenges and Solutions:
- Diagnosis remains a weak link, with millions of TB cases undiagnosed globally.
- Enhanced screening methods and adoption of rapid tests can improve TB detection efficiency.
Way Forward:
- TB control necessitates addressing transmission, infection, and progression simultaneously.
- Public education campaigns are crucial for behaviour modification regarding TB prevention.
- Enhanced Information Education Communication (IEC) activities are essential for disseminating TB prevention measures.
- Testing cohorts of schoolchildren for Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) positivity can identify infections and guide preventive treatment.
- Strong political will and comprehensive strategies integrating biomedical and socio-behavioural interventions are vital for achieving India’s TB eradication goal by
- Strengthening referral networks and notification systems and considering population mobility are vital for TB control.
- India must prioritise person-centred care, address social determinants, and embrace innovation for TB elimination.
- Collaboration between sectors and political commitment is essential for achieving the goal of a TB-free India and world.
Conclusion:
India has made progress in TB reduction, but challenges remain in diagnosis and treatment accessibility.Despite challenges, existing mechanisms and infrastructure provide hope for TB eradication.COVID-19 pandemic underscores the importance of preventive public health measures and addressing social determinants.Early diagnosis and continuous treatment accessible to all are key to changing India’s TB hotspot status.Faster implementation of new diagnostic technologies and strengthening testing capabilities are essential for TB elimination efforts.
Source: The Hindu
Mains practice question:
Discuss the challenges and potential solutions in addressing Tuberculosis (TB) in India, emphasising the importance of person-centred care, socio-economic determinants, and technological innovations. Evaluate the effectiveness of current TB control initiatives and propose actionable strategies for achieving TB elimination by 2025.