TACKLING THE FATTY LIVER DISEASE EPIDEMIC
SYLLABUS:
GS 2:
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Focus:
- The trends in fatty liver disease prevalence are alarming. MASH (Metabolic dysfunction associated steatohepatitis), a progressive form that causes liver inflammation and scarring, is expected to become the most common cause of chronic liver disease and the leading indication for liver transplantation.
Source: G7
Fatty Liver Day 2024: Key Highlights and Initiatives
|
Growing Burden of Fatty Liver Disease
- Increasing Prevalence: Global prevalence rates of Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) are estimated at 25-30%. In India, it’s even higher, affecting approximately 38.6% of adults and 36% of obese children.
- Link to Metabolic Syndrome: MASLD is closely linked to obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels, with incidence rates up to 95% in obese individuals.
- Dietary Impact: High consumption of refined carbohydrates and sugars significantly contributes to metabolic disturbances and insulin resistance, exacerbating fatty liver development.
- Progression to Serious Conditions: If untreated, MASLD can progress from simple fatty liver to severe conditions like steatohepatitis and cirrhosis, potentially requiring liver transplantation.
- Underdiagnosis: Often, fatty liver disease remains undetected until advanced stages due to the absence of early symptoms, highlighting the critical need for regular and comprehensive screenings.
Importance of Early Detection and Screening
- Comprehensive Health Screening: Early detection should include a detailed history, physical exam, and diagnostic tests such as blood work and abdominal ultrasound, which are crucial for spotting early signs of liver disease.
- Role of Ultrasound: Ultrasound is a key diagnostic tool for identifying fatty liver. However, its utility is often limited by the availability of radiologists and regulatory challenges.
- Advanced Liver Tests: Technologies like vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) should be utilized for assessing liver fibrosis, offering a non-invasive method to detect and monitor liver scarring.
- Personalized Screening Protocols: The choice and frequency of screening tests should be personalized based on individual risk factors, including family history and lifestyle.
- Integrated Screening Tools: An integrated approach combining ultrasound, metabolic screenings, and elastography can effectively detect and manage liver diseases early.
Lifestyle and Dietary Management
- Nutritional Guidance: Emphasizing a balanced diet low in refined sugars and saturated fats can prevent the worsening of liver conditions and support overall metabolic health.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps reduce obesity and improve metabolic syndrome components, thereby mitigating the risk of developing fatty liver disease.
- Weight Management: Effective weight control strategies are essential for reducing liver fat and preventing disease progression.
- Avoidance of Alcohol and Toxins: Limiting alcohol consumption and exposure to environmental toxins can prevent additional liver damage and support liver health.
- Public Health Education: Raising awareness about the impact of lifestyle choices on liver health is crucial for preventing MASLD.
Treatment and Monitoring
- Early Intervention: Timely medical intervention can halt the progression of fatty liver to more severe liver diseases.
- Regular Monitoring: Frequent follow-ups and monitoring of liver health parameters can help in adjusting treatment plans and preventing complications.
- Medications and Supplements: Certain medications and supplements might be prescribed to manage symptoms and improve liver function.
- Collaborative Care: Coordination between healthcare providers, including hepatologists, dieticians, and primary care physicians, ensures comprehensive management of the disease.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about the importance of adherence to treatment and lifestyle changes is key to successful disease management.
Policy and Healthcare System Improvements
- Increased Screening Accessibility: Ensuring wider availability and accessibility of screening tools like ultrasound and VCTE in healthcare settings.
- Policy Initiatives: Government and healthcare bodies should implement policies that promote liver health, including regulation of harmful substances and support for healthy lifestyle initiatives.
- Research and Development: Increased funding for research into the causes, prevention, and treatment of fatty liver disease can lead to better management strategies.
- Training and Resources for Healthcare Providers: Enhancing training for healthcare professionals on the latest diagnostic and treatment methods for liver diseases.
- Community Outreach Programs: Developing community-based programs that provide education and resources to prevent and manage fatty liver disease effectively.
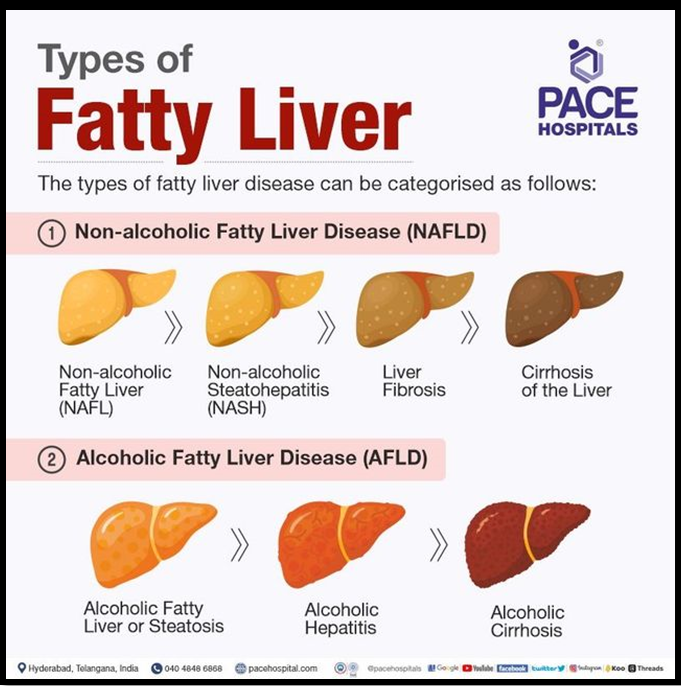
NAFLD
|
Source:Indian Express
Mains Practice Question:
“Given the increasing prevalence of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) in India, there is a growing need for integrating public health and policy initiatives. Discuss the challenges and strategies involved in incorporating health considerations into policy-making, with a special emphasis on combating the epidemic of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) among the Indian population.”
Associated Articles:
https://universalinstitutions.com/how-can-one-health-help-india-and-india-help-one-health/