SUPREME COURT TO REVIEW USE OF MONEY BILLS
Why in the news?
- Chief Justice D.Y. Chandrachud agreed to list petitions challenging the Centre’s use of Money Bills to pass contentious amendments in Parliament.
- These petitions, including those by Rajya Sabha MP Jairam Ramesh, question if certain laws can be passed as Money Bills, bypassing the Rajya Sabha
source: edurev
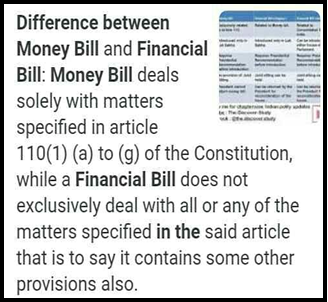
About a Money Bill:
- Definition: A Money Bill in India pertains solely to financial matters involving the Consolidated Fund of India.
- Content Scope: Includes taxation, public expenditure, public debt, borrowing regulations, and fund management.
- Constitutional Criteria: Must exclusively address specified financial subjects under Article 110.
Constitutional Provisions regarding Money Bill
About Articles in the Indian Constitution Deals with the Money Bill:
Associated Article: |