SUPERCONDUCTIVITY STUDY ON LK-99 MATERIAL
Why in the News?
- LK-99, a superconductor previously in headlines for potential room-temperature superconductivity, faced skepticism due to data issues.
- Scientists from China and Japan now report a Meissner effect in LK-99, renewing interest.
Source: Springer
Importance of Meissner Effect:
- Meissner effect, observed in superconductors, signifies expulsion of magnetic field during transition to superconducting state.
- LK-99, a copper-substituted lead apatite, displayed signs of near-room-temperature superconductivity.
- Despite hurdles, the study suggests a potential critical temperature of around -23°C for LK-99, hinting at room-temperature superconductivity.
| Key Terms
Superconductor A superconductor is a material that, at low temperatures, exhibits zero electrical resistance, allowing an electric current to flow indefinitely without loss of energy. Superconductors also expel magnetic fields from their interior during the superconducting state, known as the Meissner Effect. Meissner Effect The Meissner Effect is observed in superconductors when they transition to a superconducting state. During this transition, the material expels any magnetic field from its bulk to the surface, providing a distinctive signature of superconductivity with zero electrical resistance. |

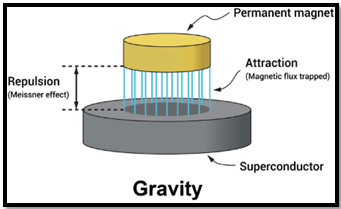 Source: Springer
Source: Springer

