Strengthening Public-Private Partnerships for Effective TB Control
Why in News ?
India, contributing 25% of the global TB burden, needs stronger public-private collaboration for better TB management. Integrating public healthcare’s standardized treatment with private hospitals’ patient-friendly approach can improve compliance, ensuring better outcomes in the fight against tuberculosis.
About TB Burden and Challenges in Treatment:
- India reports 8 million new TB cases annually, contributing to over 25% of the global TB burden.
- More than 50% of TB patients seek treatment in private healthcare facilities.
- The current treatment landscape presents two major challenges:
- Public hospitals offer free treatment but lack a welcoming environment.
- Private hospitals provide a better patient experience but are often costly and may not strictly follow standardized treatment protocols.
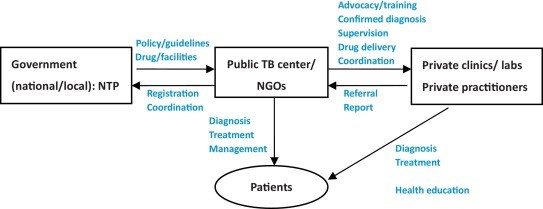
Public-Private Collaboration for Improved Care
- A hybrid model integrating public and private healthcare can enhance TB control efforts.
- Government hospitals can ensure standardized treatment, contact tracing, and access to essential medicines.
- Private healthcare facilities offer a more comfortable environment but need to improve compliance with treatment guidelines.
- Some drug-resistant TB medicines are only available in government hospitals to prevent misuse. However, mandatory hospital admission for certain cases may discourage patients from seeking treatment.
- Public-private partnerships can help create flexible care pathways, ensuring patient compliance without compromising treatment quality.
The Way Forward
- A robust system is needed to track patient care transitions, prevent gaps in treatment, and regulate unregistered practitioners.
- Diagnostic protocols should be standardized to ensure accurate TB diagnosis and treatment.
- Drug supply chains must be regulated, and strict adherence to treatment guidelines should be enforced.
- Establishing centralized monitoring of TB test results and pharmacy regulations can enhance accountability.
- Innovative approaches and reimagined partnerships will be key to achieving effective TB control in India.
National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP): Key Strategies● Goal: Eliminate TB in India by 2025, reducing incidence by 80% and deaths by 90%. ● Strategic Pillars: Detect, Treat, Prevent, and Build (DTPB). ● Strengthening Infrastructure: Increased funding, decentralized care, mobile diagnostic units. ● Capacity Building: Training healthcare workers, incentives for retention. ● Ensuring Drug Supply: Robust supply chain, regional warehouses, digital tracking. ● Tackling Drug-Resistant TB: Shorter regimens, psychosocial support. ● Community Engagement: Awareness campaigns, stigma reduction. ● Financial Support: Ni-Kshay Poshan Yojana, wage and transport assistance. ● Surveillance & Technology: AI-driven monitoring, Ni-Kshay platform. ● Multi-Sector Collaboration: Nutrition, sanitation, housing, industry involvement. |