“STRATEGIC IMPERATIVES: DEVELOPING INFRASTRUCTURE IN THE ANDAMAN AND NICOBAR ISLANDS”
Syllabus:
- GS-2-India and its foreign policy, Relations with global powers ,ensuring sovereignty
Focus :
- The new thrust on developing strategic infrastructure, both civilian and military, on the Andaman and Nicobar Islands is decades overdue.This gives an insight on how to develop the islands .
Source- ToI
Introduction
- Shift from Look East to Act East policy
- Growing significance of ocean power
- Need for strategic development in Andaman and Nicobar Islands
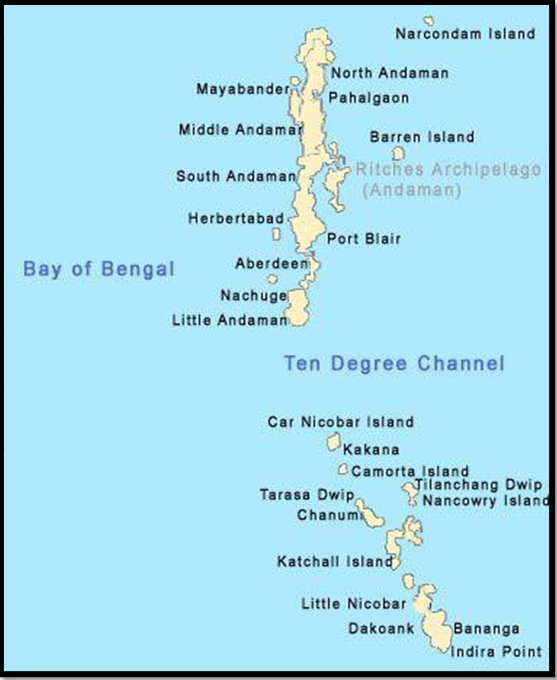
Strategic Importance of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Geopolitical location and proximity to key maritime routes-The islands are located 700 nautical miles (1,300 km) southeast of the Indian mainland. The Malacca Strait, the main waterway that connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific, is less than a day’s steaming from Port Blair.
- Sabang in Indonesia is 90 nautical miles southeast of Indira Point (on Great Nicobar island), and Coco Island (Myanmar) is barely 18 nautical miles from the northernmost tip of the Andamans.
- Significance as chokepoints in the Indo-Pacific region– Should Thailand build the Kra Canal connecting the Gulf of Thailand with the Andaman Sea, its mouth would be about 350 nautical miles east of Port Blair.
- Territorial waters and maritime zones under Indian jurisdiction– The islands share four of India’s interna- tional maritime zone delimitations with Myanmar, Thailand, Indonesia, and Bangla desh. They also give India substantial ocean space under the United Nations Conference on the Laws of the Sea (UNCLOS) in terms of exclu- sive economic zone and continental shelf.
Historical Neglect and Slow Development
- Lack of strategic vision post-independence
- Recent recognition of islands’ strategic importance
- Challenges in infrastructure development: distance, environmental clearances, coordination issues
Priorities for Strategic Infrastructure Development
- Surveillance and security of islands
- Deterrence against naval threats
- Economic development of southern islands
- Improved transportation and connectivity
- Reduced dependence on mainland support
Key Infrastructure Projects Needed
- Airfields with long runways
- Ports and fuel storages in northern and southern groups
- Enhanced military presence and assets
- Galathea Bay transhipment port
- Development of maritime services and logistics
- Road networks, ferry services, and seaplane terminal
Initiatives taken
|
Strategies for Accelerating Development
- Sourcing materials and expertise internationally
- Streamlining forest and environmental clearances
- Extending concessions for defence infrastructure
- Encouraging planned habitation of uninhabited islands
- Leveraging international partnerships such as the Quad and Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative
Conclusion
- Urgency of strategic infrastructure development in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Need for coordinated efforts and proactive measures
- Potential benefits for India’s maritime security and economic growth
Source:Indian Express
Mains Practice Question :
GS-3
“Discuss the strategic importance of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands for India’s security and the challenges and priorities in developing strategic infrastructure in these islands. Evaluate the strategies needed to accelerate infrastructure development and enhance India’s maritime capabilities in the region.” (250 words)